The basic function of a RESTful API is the same as browsing the internet. The client contacts the server by using the API when it requires a resource. API developers explain how the client should use the REST API in the server application API documentation. These are the general steps for any REST API call:
-
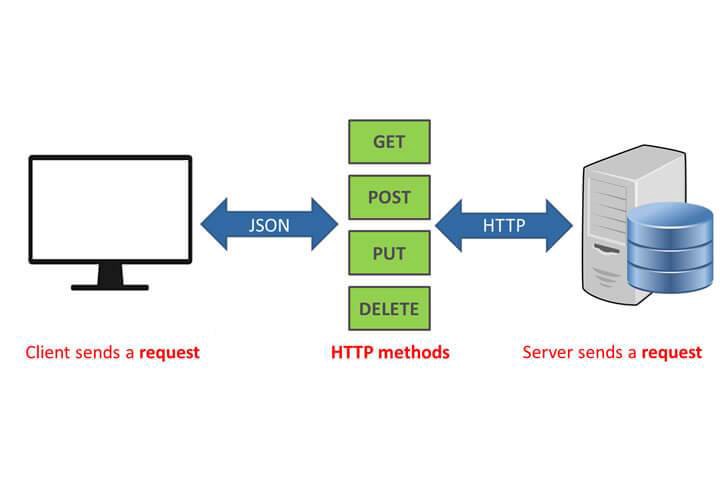
The client sends a request to the server. The client follows the API documentation to format the request in a way that the server understands.
-
The server authenticates the client and confirms that the client has the right to make that request.
-
The server receives the request and processes it internally.
-
The server returns a response to the client. The response contains information that tells the client whether the request was successful. The response also includes any information that the client requested.
The REST API request and response details vary slightly depending on how the API developers design the API.
RESTful APIs client requests contain the following main components:
-
The server identifies each resource with unique resource identifiers. For REST services, the server typically performs resource identification by using a Uniform Resource Locator (URL).
-
The URL specifies the path to the resource. A URL is similar to the website address that you enter into your browser to visit any webpage. The URL is also called the request endpoint and clearly specifies to the server what the client requires.
- Developers often implement RESTful APIs by using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). An HTTP method tells the server what it needs to do to the resource.
- The following are four common HTTP methods:
Clients use GET to access resources that are located at the specified URL on the server. They can cache GET requests and send parameters in the RESTful API request to instruct the server to filter data before sending.
Clients use POST to send data to the server. They include the data representation with the request. Sending the same POST request multiple times has the side effect of creating the same resource multiple times.
Clients use PUT to update existing resources on the server. Unlike POST, sending the same PUT request multiple times in a RESTful web service gives the same result.
Clients use the DELETE request to remove the resource. A DELETE request can change the server state. However, if the user does not have appropriate authentication, the request fails.
Request headers are the metadata exchanged between the client and server. For instance, the request header indicates the format of the request and response, provides information about request status, and so on.
REST API requests might include data for the POST, PUT, and other HTTP methods to work successfully.
RESTful API requests can include parameters that give the server more details about what needs to be done. The following are some different types of parameters:
- Path parameters that specify URL details.
- Query parameters that request more information about the resource.
- Cookie parameters that authenticate clients quickly. Aachal G