Written by Aditya Rajguru and Gerardo Rodriguez for the completion of the embedded systems course at the University of Texas at Arlington.
There is an increasing demand in automation in the present manufacturing industry. Specifically, there is an increasing demand in cheap automation. We have developed a device that industries with color-detecting needs may find useful. This device is called a colorimeter.
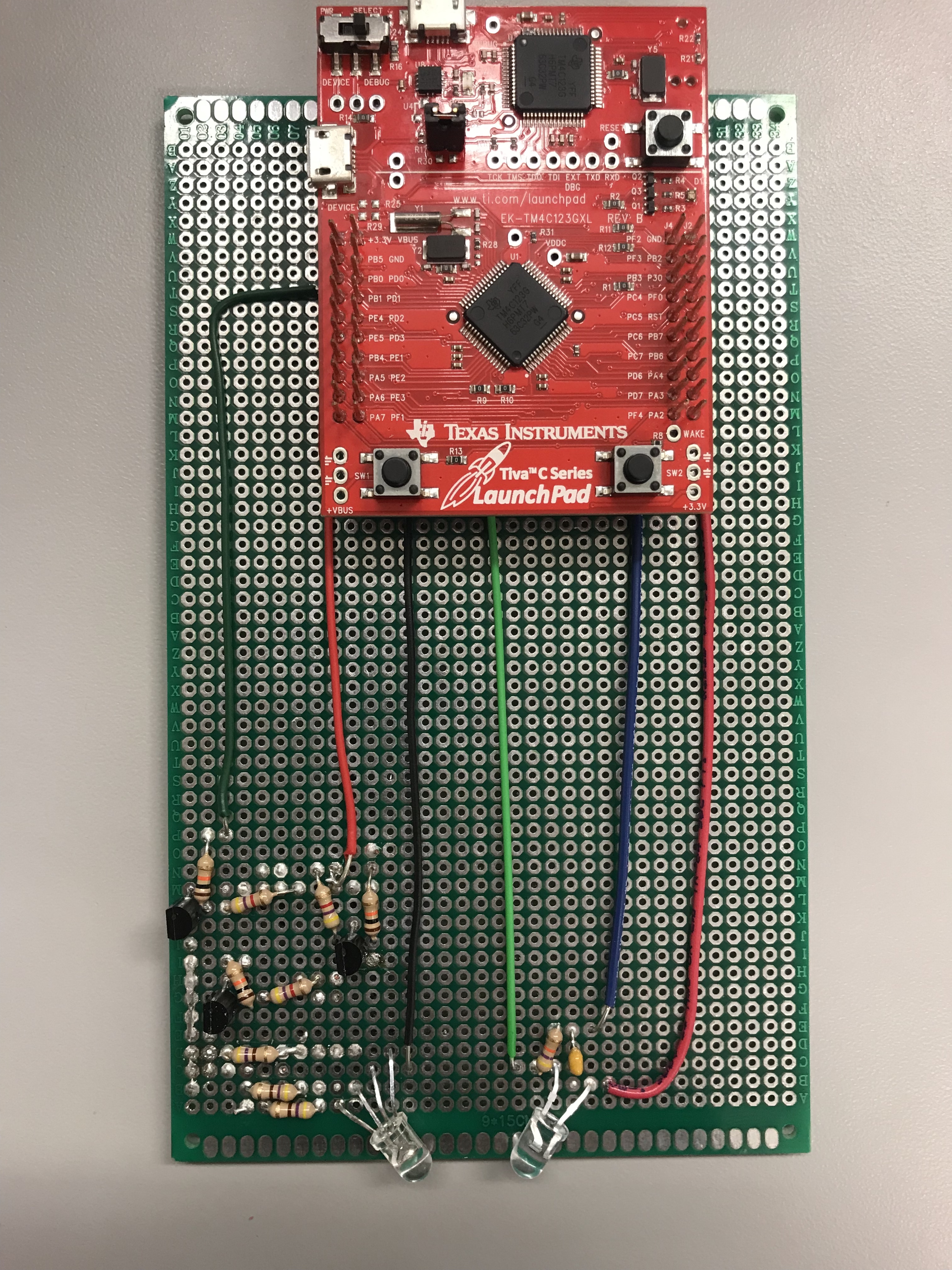
This device is implemented with a Tiva C TM4C123GXL Launchpad from Texas Instruments. Circuitry was designed and implemented along with the board as well. Below, you'll find the relevant circuits used in the device.
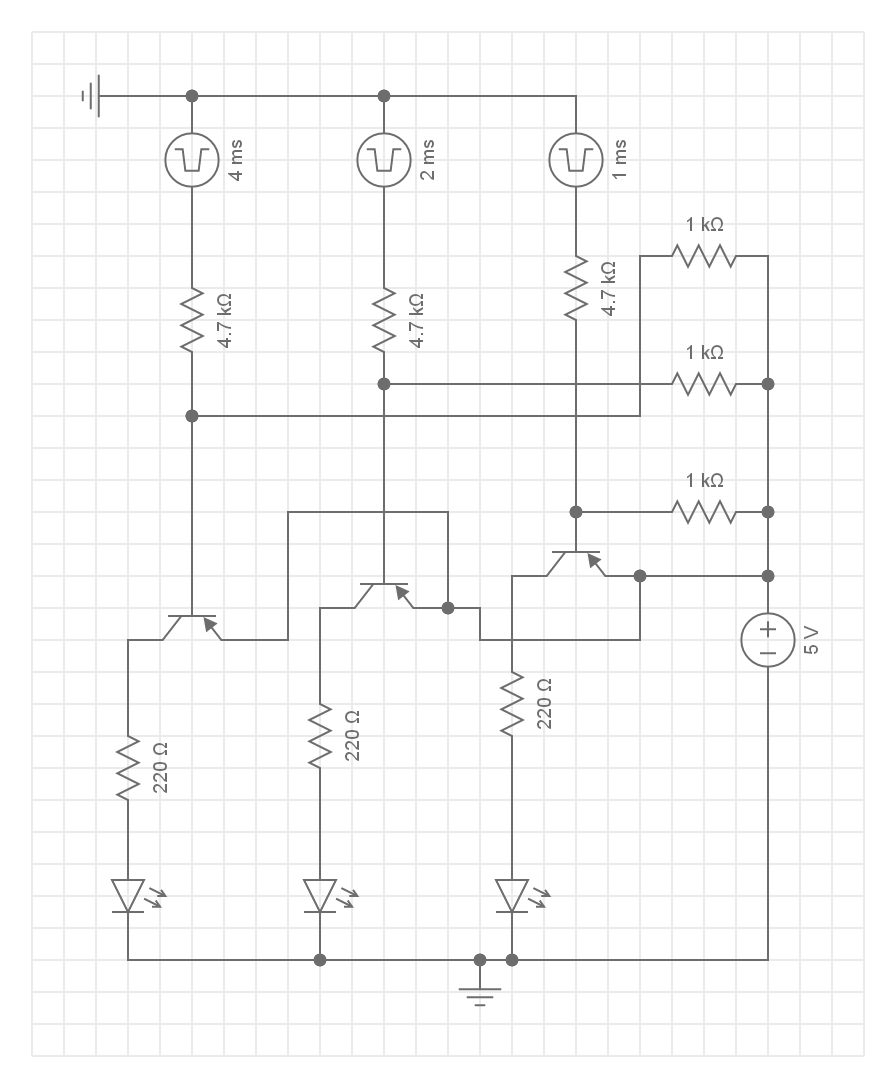
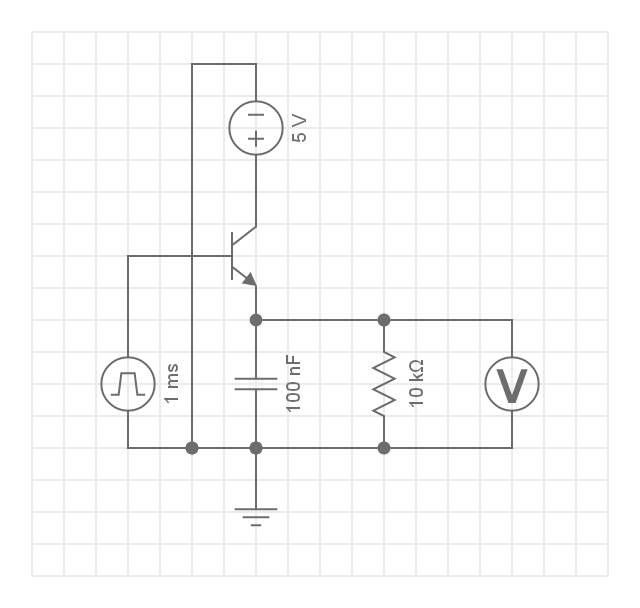
The square waves represent the pulse-width-modulated signals that the board sends to adjust the power delivered to a specific light-emitting diode. Along with this circuit, a separate circuit was designed and implemented to detect similarly —or dissimilarly— colored surfaces.
Here, the voltmeter is a placeholder for the port responsible for receiving analog input from the phototransistor. The BJT transistor is a placeholder for the phototransistor and the square wave is a placeholder for the light source coming from the tri-color LED.
The two circuits are placed adjacent to each other so that light from the tri-color LED can be reflected off of a surface and directed towards the phototransistor. Any light not absorbed by the surface of interest will strike the phototransistor. Below is an image of the physical board sans the spacers used to direct the light.
The transistors to the LEDs are driven by the digital ports on the board. These digital ports send out pulse-width-modulated signals; these signals are capable of adjusting the brightness on each LED due to the characteristic equation
VI * t = E.
A constant current and voltage turned on for an arbitary amount of time will vary the energy output. This discrete signal will then be captured by the phototransistor placed on the other side of the board. The phototransistor, coupled with a resistor and a capacitor, will then smooth out the square wave to a more consistent semi-sine wave signal.
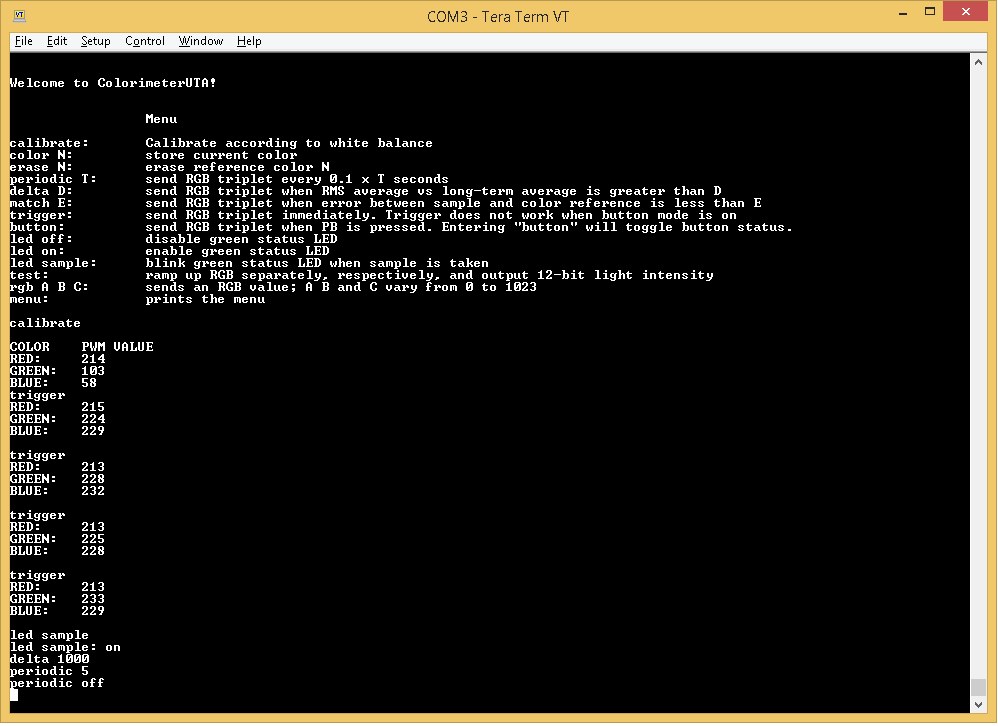
The interface of the colorimeter is text-based. Any terminal capable of communicating over the universal asynchronous reader transmitter interface is capable of communicating with the board while running the program. To communicate properly, the terminal must be sending and receiving at a Baud rate of 115,200 with 8 data bits, 1 start bit, and 1 stop bit. Furthermore, the commands must not exceed a string length of 80 bytes. Below is a screen capture of the terminal after being calibrated.
The board comes with a variety of functions. Referencing from the image above:
When provided with a white-balance, the device will increase the brightness of each LED until the port connected to the phototransistor reaches a raw threshold value. For this device, the threshold is 511 for greater resolution. Furthermore, a distance of about 10 millimeters from the surface of interest is required to properly work with the board.
When the colorimeter is pointed towards a surface, entering color N such that N is an integer from 0 to 31, the colorimeter will send an RGB triplet to the surface, read the values from the analog pin, and store the three values into memory location N to reference later.
The device will erase whatever is stored in memory location N such that N is an integer from 0 to 31.
The device, when stimulated by a user-specified interrupt, will send an RGB triplet every 0.1 * T seconds such that T is an integer from 0 to 255 or off. This function is the sampling function that must be initiated after delta and match are specified. This means that, for example, the command periodic 1 will sequentially flash the LEDs on the tri-color LED every millisecond.
The device will turn on RGB reporting when the root-mean-square and the long-term average (otherwise known as the infinite impulse response) deviate by more than D such that D is an integer from 0 to 255. This feature is useful if a user desires to detect inconsistencies in a rather consistent environment. An example could be a crayon manufacturing plant. The colors of the crayons are relatively consistent but a factory worker may be interested in finding any crayons that don't generally look like the rest.
This function must be used in conjunction with periodic T; if delta is not specified by the user before periodic is turned on, then delta will be initialized to 0.
The device will report if a match is found when the error between a sample and one of the color references is less than E such that is an integer from 0 to 255.
Like delta D, this function must be used in conjunction with periodic T; if match is not specified by the user before periodic is turned on, then match will be initialized to 0.
The device will send an RGB triplet whenever trigger is entered by the user. Each LED is on for 10 milliseconds making the device very responsive to fast-moving objects. This makes the device a very desirable one for assembly line automation. The trigger command does not work when button mode is on.
The device will send an RGB triplet whenever the pushbutton SW1 on the board is pressed and after the button command has been sent to the device. The trigger command does not work —by design— when button mode is on. To turn button mode off, simply enter button again.
The button command works with an interrupt and a debounce checker. The device will check every 10 milliseconds if the pushbutton is pressed. After the device checks for the 15th consecutive time, if the pushbutton is still pressed, then the device sends a trigger command to the LED.
The device will turn off the onboard LED.
The device will turn on the onboard LED.
The device will toggle the LED every time the trigger command is issued. Entering led sample once will turn the LED sampling mode on. Entering led sample a second time will turn the LED sampling mode off.
The device will ramp up each LED from the tri-color LED and print out the associated pulse-width-modulated value and its corresponding raw analog value. This command is used to determine a viable threshold for the calibrate command. It is ideal to run this command whenever setting up the device in new working conditions.
The device will send a pulse-width-modulated value to each LED specified by the arguments A, B, and C. A, B, and C must be values from 0 to 1023.
This command prints the menu onto the terminal screen. Equivalent to a help command on other systems, machines, or devices.
The conditions needed for this device to properly work are temperatures between 20ºC to 80ºC, a room with low ambient lighting, and a computer capable of running a terminal or a terminal emulator. The surfaces must be 10 millimeters away from the device for optimal operation.