This project aims at providing a comprehensive, open source anonymization framework for (tabular) sensitive personal data using selected methods from the broad area of statistical disclosure control. The basic idea is to transform datasets in ways that make sure that they adhere to well-known formal privacy criteria. Typical examples include k-anonymity, l-diversity, t-closeness and d-presence. For data transformation ARX implements a combination of generalization and suppression. For generalizing data items, the framework employs generalization hierarchies, which can easily be constructed by end-users to meet their requirements. Because ARX is highly efficient in terms of execution times, it enables users to explore a large number of possible privacy-preserving transformations in near real-time and pick the one that best suits their needs (i.e. a specific usage scenario).
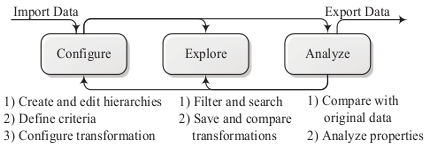
ARX supports all major aspects of data anonymization. These different aspects are combined in a multi-step process that allows users to iteratively adjust parameters, until the result matches their requirements. As depicted in the above figure, the basic steps consist of 1) configuring the anonymization process, 2) exploring the solution space and 3) analyzing the transformed data. In the configuration phase, the input data is loaded, generalization hierarchies are imported or created and all further parameters, such as privacy criteria, are specified. When the search space has been characterized by executing the anonymization algorithm, the exploration phase allows searching the solution space for privacy-preserving data transformations that fulfill the user’s requirements. To assess suitability, the analysis phase allows comparing transformed datasets to the original input dataset. Based on this analysis, further solution candidates might be considered and analyzed, or the configuration of the anonymization process might be altered. ARX consists of several components:
- An open source implementation of a highly efficient k-anonymity, l-diversity, t-closeness and d-presence algorithm.
- A dedicated data management framework, that has been carefully engineered to meet the needs of data anonymization algorithms and can serve as a testbed for further research.
- A clean API that brings powerful data anonymization capabilities to any Java program.
- A comprehensive cross-platform graphical user interface (GUI), which is oriented towards end-users and provides several advanced features, such as a wizard for creating generalization hierarchies, an intuitive way to explore the solution space and ways to assess the utility of transformed datasets.
ARX currently distinguishes between four different types of attributes:
- Identifiying attributes (such as name) can be removed from the dataset.
- Quasi-identifying attributes (such as age or zipcode) are generalized and/or suppressed by applying the provided generalization hierarchies.
- Sensitive attributes are kept as is and can be used to enforce t-closeness or l-diversity.
- Insensitive attributes are kept as is.
ARX implements combined support for two specific types of transformation methods: multi-dimensional global recording with full-domain attribute generalization and local recoding with tuple suppression. This method is easy to understand by users and allows providing several advanced options for configuring and parameterizing the transformation process. Additionally, this transformation method enables ARX to completely classify the solution space and automatically determine the transformation with optimal data utility. To this end, it implements a broad spectrum of methods for measuring data utility (i.e. loss of information induced by transformations).
ARX provides highly efficient implementations of several well-known privacy criteria as well as data utility metrics. Moreover, ARX supports arbitrary combinations of privacy criteria. In most cases, it outperforms previous implementations by up to several orders of magnitude. It is able to find optimal solutions for monotonic and non-monotonic privacy criteria and utility metrics (e.g. l-diversity, t-closeness and d-presence with tuple suppression). When enabling tuple suppression, a subset of the data items is allowed to not adhere to the specified privacy criteria. During the anonymization process this subset is removed from the dataset, as long as the total number of suppressed tuples is lower than a user-defined threshold. This allows to further reduce information loss. With implementations of classic k-anonymity as well as various variants of its extensions, such as l-diversity, t-closeness and d-presence, ARX’s coverage of privacy criteria and utility metrics is unmatched in the area data anonymization tools. Variants of l-diversity include recursive-(c,l)-diversity, entropy-l-diversity and distinct l-diversity. The t-closeness criterion can be based on the earth mover’s distance with equal or hierarchical ground distance (using generalization hierarchies). Generalization hierarchies can be represented in a functional manner, enabling support for continuous attributes and advanced means for measuring data utility. The supported utility metrics include AECS, discernibility, precision, non-uniform entropy and loss. Our codebase is extensively tested (~1000 unit tests), well documented and suitable for implementing a wide variety of data anonymization algorithms.
ARX Anonymization Tool
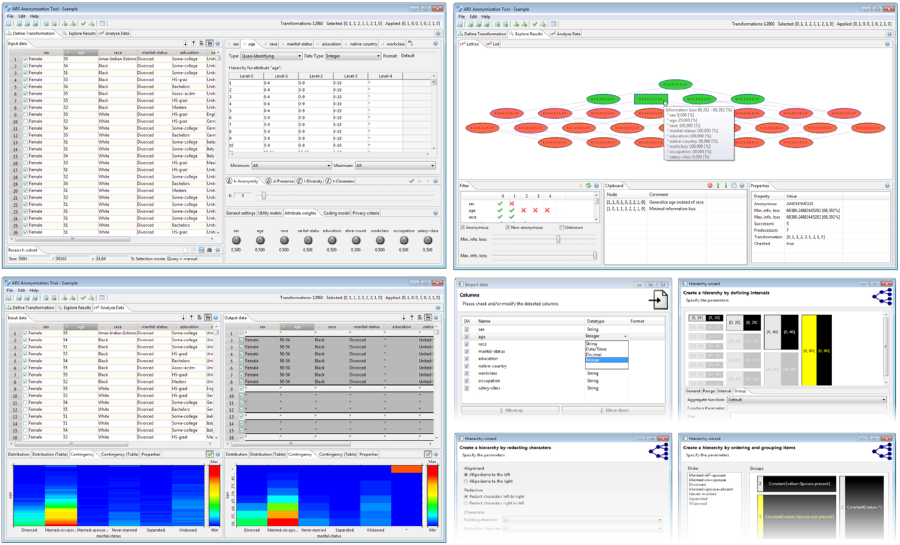
Our cross-platform anonymization tool provides an intuitive graphical interface for end-users and implements advanced features, such as wizards and a context-sensitive help.
The graphical user interface supports the three steps from the anonymization process described in the previous section by implementing three dedicated perspectives.
ARX Software Library
// Load data
Data data = Data.create("input.csv");
// Set attribute types and load hierarchies
data.getDefinition().setAttributeType("age", Hierarchy.create("age.csv"));
data.getDefinition().setAttributeType("zipcode", Hierarchy.create("zipcode.csv"));
data.getDefinition().setAttributeType("disease", AttributeType.SENSITIVE_ATTRIBUTE);
// Define privacy requirements
ARXConfiguration config = ARXConfiguration.create();
config.addCriterion(new KAnonymity(5));
config.addCriterion(new HierarchicalDistanceTCloseness("disease", 0.6d, Hierarchy.create("disease.csv")));
config.setMaxOutliers(0d);
config.setMetric(Metric.createEntropyMetric());
// Perform anonymization
ARXAnonymizer anonymizer = new ARXAnonymizer();
ARXResult result = anonymizer.anonymize(data, config);
// Write result
result.getHandle().write("output.csv");More examples are also available in the repository.
Specific limitations
- ARX implements in-memory data management, meaning that the dataset that is to be anonymized must fit into a machine’s main memory. This should normally not be a problem, as ARX can handle datasets with several million entries on current commodity hardware. For very large datasets, memory consumption may be reduced by removing attributes that are insensitive and irrelevant to the anonymization process. If these must be re-integrated after the de-identification process, a tuple identifier can be introduced. Moreover, ARX implements a space-time trade-off that may be used to reduce memory consumption.
- ARX currently relies on a globally-optimal search strategy and currently materializes the complete solution space. As a consequence, it can only handle anonymization problems in which the search space is small enough to allow materialization. As a rule of thumb ARX can handle datasets with up to ~15 quasi-identifiers, but this depends on the size of the generalization hierarchies utilized. In the near future ARX will be extended with methods that overcome this limitation.
General limitations
- Data anonymization is a complex issue that must be performed by experts. There is no single measure that is able to protect datasets from all possible threats, especially not while being flexible enough to support all usage scenarios. As is common in IT security, data controllers should therefore follow the “onion layer principle” and employ a multitude of measures for protecting sensitive personal datasets. This includes legal agreements as well as “data economy”, meaning the principle that nothing more than those details may be collected, stored and shared which are absolutely essential.
- The anonymization techniques implemented by ARX can be an important building block for protecting sensitive personal datasets, but they can only provide very specific guarantees which require rather strong assumptions to be made about the goals and the background knowledge of an attacker. Alternative methods, such as Differential Privacy, require much less such assumptions but usually involve stronger trade-offs in terms of utility or supported workflows.
More information can be found on our website at: http://arx.deidentifier.org/
The ARX framework is copyright (C) 2012-2015 Florian Kohlmayer and Fabian Prasser. It is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0:
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
The framework uses external libraries. The according licenses are listed in the respective lib folders.