這裡留下學生曾經問過的問題所延伸的解釋筆記,歡迎共同補充。
這篇講在這門課會遇到的小東西。
TAFree是一個線上程式批改系統專案,不為什麼而做,純屬為了「解放助教」(後來開發時期delay卡到提thesis proposal的時間,所以就順便寫成論文)。專案裡面目前有6個人,都是從曾經上過這門課的學生挖來的,裡面的人沒有多神,但是有很多熱忱。我們非常歡迎覺得系統很爛的人加入改良,或是砍掉重練也可以。
- 編譯時期錯誤(Compiling Error) 就是語法錯誤,通常在Eclipse Run之前就會被Eclipse AST機制發現。
- 執行時期錯誤(Runtime Error)
- 陣列索引太大或太小使得陣列的操作爆掉。
- 需要輸入浮點數,卻用nextInt()。
- 其他所有Run之後才出問題的事情。
- Compile and Runtime Errors in Java
- 排版 Ctrl+Shift+F可以縮排整份source code。
- 改類別名稱 游標移到該檔案點右鍵,選Refactor。
Java™ Platform, Standard Edition 8 API Specification
解釋for-each和傳統for loop的差別。
以下用範例說明這兩種用法要注意的事情
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3 };
for (Integer e : numbers) { // Enhanced for loop (for-each)
System.out.print(e + " ");
e = e * 2;
}
System.out.print("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) { // What does for-each exactly do...
Integer e = numbers[i];
System.out.print(e + " ");
e = e * 2;
}
System.out.print("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) { // Traditional for loop
System.out.print(numbers[i] + " ");
}
System.out.print("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) { // Traditional for loop for changing elements in array
numbers[i] = numbers[i] * 2;
System.out.print(numbers[i] + " ");
}
}
}首先要分辨e跟numbers的元素是不是存在電腦裡的相同記憶體位址?
若不是,當我們操作e就無法改變到numbers裡的元素了。
在範例裡面:
第一個迴圈是enhanced for loop的用法。
第二個迴圈是把第一個迴圈打回原貌。
我們看第三個迴圈印出來的東西,可以知道foreach改變不了numbers,於是我們用第四個迴圈才能達到我們真正想要的操作 。
如果是只想要「取出」陣列裡的值,把它們印出來或是存到別的變數裡,就可以用for-each;如果要「改變」陣列裡的值,就必須用傳統的for loop寫法。
這篇只講Java,別種語言的物件導向實作方式「不一定」是這樣。
不負責任推諉結束,請繼續看下去。
static是相對於this的關鍵字。this用來代表屬於「這個物件」的成員,static用來代表屬於「這個類別」的成員。我們用個範例來解釋這一切。
範例輸出:
This can not be called in main
Dog1's breed: Labrador
Dog1's leg: 6
Dog2's breed: Labrador
Dog2's leg: 6
This can be called in main
範例源始碼:
public class Dog{
public String name;
static String breed="Dachshund"; // It is public
private static int leg=4;
private String color;
public Dog(){
// Create a TestDog object
TestDog testdog = new TestDog();
testdog.callMe();
}
public Dog (String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setColor(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void setLeg(int n){
// We can not use this.leg because it is static
leg = leg + n;
}
public int getLeg(){
// We can not use this.leg because it is static
return leg;
}
}
class TestDog{
public static void main(String[] args){
// Create one dog with argument
Dog dog1 = new Dog("Bibi");
dog1.breed = "Labrador";
// Create another dog without argument
Dog dog2 = new Dog();
dog2.setLeg(2);
System.out.println("Dog1's breed: " + dog1.breed);
System.out.println("Dog1's leg: " + dog1.getLeg());
System.out.println("Dog2's breed: " + dog2.breed);
System.out.println("Dog2's leg: " + dog2.getLeg());
callMeInMain();
}
public static void callMeInMain(){
System.out.println("This can be called in main");
}
public void callMe(){
System.out.println("This can not be called in main");
}
}然後你就有一堆疑問...
- 沒寫public或private就預設為public 例如breed被預設是public,所以TestDog的main()就可以直接用dog1.breed。
- 前置static的data field會屬於類別 我們看到 dog1更新了Dog的品種,而dog2更新了Dog的腿數,因此最後不論是dog1或是dog2的品種都是拉布拉多並且有6條腿,這就是因為我們是直接更新了Dog的static成員。
- 前置static的method裡面只能呼叫其他也前置static的method TestDog的main()只能呼叫callMeInMain()卻不能呼叫callMe(),這是因為main()是static method所以只能用也是static的method。
- 前置static的method在其他類別中就沒有限制 我讓Dog()去呼叫TestDog的callMe()是沒有問題的。
- abstract class宣告abstract method的時候 abstract class的method可以是非抽象方法,但至少有一個抽象方法。
- interface宣告method的時候 interface的method只能是「公開(public)」「抽象(abstract)」的方法。
- 一般class定義method的時候 No way。
- @開頭的東西是「標註(Annotation)」,用來請編譯器幫我檢查東西。
- @Override使用時機 我只想得到怕手滑打錯要覆寫的method名字,所以請編譯器幫我檢查。
回答這個問題之前,要先有兩個觀念:
1. class定義裡面只有兩種東西: data field和method然後就沒有了
(至少在這個課程不會遇到其他東西, 除非要寫內部類別)
如果你對這句話有疑慮,可能是因為沒搞懂:
- main method是程式的進入點
- constructor是method,例如:
class Ship{
Ship(){} // 這東西叫建構子,它是一個沒有回傳東西的public method
}2. class定義放在哪裡,會導致誰才有權限使用它?
接著,我們要開始回憶我們總共遇過哪幾種class
-
Java寫的,例如: Scanner Scanner放哪裡? Scanner提供我們各種應付標準輸入型態的method,所以可想而知它很大,很大就要壓縮,所以Scanner跟其他跟它類似的東西被壓縮成.jar檔,放在函式庫裡面。因為Eclipse有自動抓取電腦裡的JRE(JRE裡面有很多.Jar),所以你可安心的在Eclipse使用Scanner。(不相信你可以看你開的project裡面有個JRE的資料夾)
-
我們自己寫的,例如: Rectangle
我們可以把它放在哪裡?-
某個Class的定義裡嗎? 不行! (別忘了1.說過class定義裡只有data field和method然後就沒有了!)
-
某個method裡嗎? 可以,但是那個class的定義必須要放在要new它的物件之前(因為要先讀得到它的定義嘛!)。可是這樣做會發生什麼事情?如果我們new很多不同的class,然後這些不同class又彼此有很複雜的牽涉關連,我們會搞混到底class的定義誰先誰後,所以不建議這麼做。
-
某個public class的定義外面: 這樣又分成兩種: 在同package下,放同一份檔案或是開另外一份檔案?
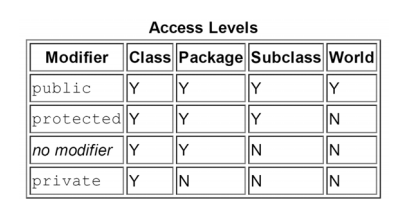
在回答這個問題之前,我們要先搞懂class的權限修飾
就是說class會依據它前面是public、private、沒有寫等等的不同而決定誰可以用它。
-
-
public class 全世界都可以用它。
所以把所有class的權限調成public是最安心的嗎?但是別忘了一個.java檔只能出現一個public class。 -
private class 只有 class自己本身可以用它自己。
什麼意思? 如果要使用這個class,勢必要在別的class的某個method(例如main)去new它,對不對? 但是只有它自己才能用它自己,所以當然沒辦法在別的class去new它。 -
沒有寫,只要是同package的其他class才可以使用它。
-
Protected,教繼承再講…
現在可以回答,class的定義要放哪裡了?
如果你希望同package下的其他class都可以用某個class,那麼那個某個class就可以不要加上權限修飾或是加上public在另一份檔案。
記得,同一個package下不可以寫兩個一樣名字的class(無論是public或沒有寫權限)。
(後記:開心的話也可以把自己寫的class壓成.jar匯入project的library喔!)
- 繼承(Inherit)和介面(Interface)的存在是為了避免重複設計。
- 繼承跟介面不一樣的地方:
| 繼承 | 介面 | |
| 關鍵字 | extends | implements |
| 關係 | 是一種 | 擁有行為 |
| 白話文 | 只可以繼承一個類別 | 可以實作很多個介面 |
- 多型(Polymorphism)就是一個物件在執行時期可以被當成不只一種型別(類別)。
講個沒弄懂多型會發生Runtime Error或Compiling Error的例子:
public class RPG {
public static void main(String[] args){
SwordsMan role1 = new SwordsMan();
Role role2 = new SwordsMan();
SwordsMan role3 = new Role(); //編譯時期被靠北
Role role4 = new SwordsMan();
SwordsMan role5 = role4; //編譯時期被靠北
Role role6 = new SwordsMan();
SwordsMan role7 = (SwordsMan)role6;
Role role8 = new Magician();
SwordsMan role9 = (SwordsMan)role8; //編譯通過 但是執行時期被靠北
}
}[1] 林信良 (2014)。Java SE 8 技術手冊。GOTOP Information Inc。
每當我們創建物件時其實我們是在幫一堆位元資料找一個家安置,而那個家就是俗稱的記憶體位置。
Object o = new Object(); 以下示範物件何時會隨著「=」搬家:
After tmpLine = lines[i - 1];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@6d06d69c
Indexed Line is at Line2D@6d06d69c
After lines[i - 1] = lines[j];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@6d06d69c
Indexed Line is at Line2D@7852e922
After tmpLine = lines[i - 1];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
Indexed Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
After lines[i - 1] = lines[j];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
Indexed Line is at Line2D@6d06d69c
After tmpLine = lines[i - 1];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
Indexed Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
After lines[i - 1] = lines[j];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
Indexed Line is at Line2D@70dea4e
After tmpLine = lines[i - 1];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
Indexed Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
After lines[i - 1] = lines[j];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
Indexed Line is at Line2D@5c647e05
After tmpLine = lines[i - 1];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
Indexed Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
After lines[i - 1] = lines[j];
Temporary Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
Indexed Line is at Line2D@4e25154f
直接看碼:
public class TestLine2D {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Line2D[] lines = new Line2D[5];
for (int i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
lines[i] = new Line2D(Math.random() * 10, Math.random() * 10, Math.random() * 10, Math.random() * 10);
}
printInShuffle(lines);
}
public static void printInSequence(Line2D[] lines){
for(Line2D line: lines){
System.out.print(" " + line.getLength());
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
public static void printInShuffle(Line2D[] lines){
Line2D tmpLine;
for(int i = lines.length ; i >= 1 ; i--){
int j = (int)(Math.random() * i);
tmpLine = lines[i - 1];
System.out.println("After tmpLine = lines[i - 1];");
System.out.println("Temporary Line is at " + tmpLine);
System.out.println("Indexed Line is at " + lines[i-1]);
lines[i - 1] = lines[j];
System.out.println("After lines[i - 1] = lines[j];");
System.out.println("Temporary Line is at " + tmpLine);
System.out.println("Indexed Line is at " + lines[i-1]);
lines[j] = tmpLine;
}
}
}
class Line2D {
private double x1;
private double y1;
private double x2;
private double y2;
private double length;
Line2D(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2){
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.length = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(y2-y1, 2) + Math.pow(x2-x1, 2));
}
public double getLength(){
return this.length;
}
}在Java舉凡能夠視為整數值的型別(int、long、short、byte、char)變數都可以被轉成二進位制以Bitwise Operator操作,例如
int a=1;
a *= 2;等價
a <<= 1;因為a <<= 1比a *= 2快,所以通常越是底層的Library就越常看見開發人員偏好二進位操作,我們不希望一個很基本的函式由於實作方式太耗時間就拖垮了那些使用它的程式。
- ^ XOR Bitwise Operator:
| Operand1 | Operand2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
- & AND Bitwise Operator
| Operand1 | Operand2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
- | OR Bitwise Operator
| Operand1 | Operand2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
-
<< Left Shift Operator 「a<<b」代表a向左移b個位置,其右邊補b個0。
-
>>> Unsigned (Logical) Right Shift Operator 「a>>>b」代表a向右移b個位置,其左邊補b個0。
-
>> Signed (Arithmetic) Right Shift Operator 「a>>b」代表a向右移b個位置,其左邊補原本最左邊的位元值。
Java的int變數佔4個byte,也就是32個bit,每個bit上面不是0就是1。
例如
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 = 1
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000010 = 2
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000100 = 4
聰明如你,那負整數怎麼辦?
所謂的二補數系統,就是在能夠表達負整數的那麼多種系統中的其中一個系統而已。
它的特徵就是把最左邊的位元當作正負號,1代表負數,0代表正數。
例如
10000000 00000000 00000000 00000001是負的。
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001是正的。
再來是知道正負號之後,它的絕對值怎麼算呢?
- 正整數之前講過了
- 負整數的遊戲規則就是,遮掉最左邊的負號,把剩下的位元值取補數,再加1。 例如
10000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
= (-1) * (1111111 11111111 11111111 11111110 + 1)
= (-1) * ((2^1 + 2^2 + 2^3 + ... + 2^29 + 2^30) + 1) = -2147483647
從二進位的角度,我們可以輕易地猜出int的最大正整數值及最小負整數值。
-
int最大正整數
01111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 = 2147483647 -
int最小負整數
10000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 = -(2147483647+1) = -2147483648 -
那0呢?
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 = 0
- 把左移 << 看成是 乘2的幾次方
例如
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000110 = 6
往左移4個位置
00000000 00000000 00000000 01100000 = 96 = 6 * (2^4)
但是!!!移過頭就不見了喔 如果把6左移100個位置,答案會是0喔(不會循環的意思)。
- 把右移 >>> 看成是 除2的幾次方
例如
00000000 00000000 00000000 01100000 = 96
往右移4個位置
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000110 = 6 = 96 / (2^4)
但是!!!失去的不一定能找回來
如果把
11111000 00000000 00000000 00000000 = -134217728
向左移4個位置
10000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 = -2147483648
再向右移4個位置
00001000 00000000 00000000 00000000 = 134217728
答案可是不會變回來的喔
- 把右移 >> 看成是 除2的幾次方 並且 保留原來的正負號
例如
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111110 = -2
往右移1個位置,右邊再補滿原本的符號,即1(負號)
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 = -1 = -2 / 2
原本是負的右移之後還是負的喔
聰明如你,原本是正的右移之後也會是正的。
What are bitwise shift (bit-shift) operators and how do they work?
我們知道Java提供兩種方式讓我們產生亂數:
- java.lang.Math
- java.util.Random
這兩者「使用」上,最大的差別是Random可以設亂數種子,但是當程式設下亂數種子後,發現每次產生的數字序列竟然是固定的?可是,亂數不是應該要很亂嗎?
直接看碼:
import java.util.Random;
public class TestRandom {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random(20);
System.out.print("nextInt(): ");
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
System.out.print(" " + random.nextInt());
}
System.out.print("\nnextInt(45): ");
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 10; i++){
System.out.print(" " + random.nextInt(45)); // Generate 0~44 positive integer
}
}
}不管執行幾百遍都是輸出這樣:
nextInt(): -1150867590 -1704868423 884779003 -29161773 -885414485 -1791719506 700408466 -1654940986 665796387 -1584522320
nextInt(45): 41 32 5 0 8 41 24 28 7 21
如果我們把創建Random物件的方式改為no-arg constructor:
Random random = new Random();每次的執行結果就會不一樣了。
由於網路上難找解釋技術實作好讀的文章,所以就不想再花力氣另外寫導讀了,請自行閱讀電腦的隨機數是如何做到的?,有個概觀後,就來看Java又是怎麼實作Random的呢?
我們去看GNU維護的類JDK所提供的java.util.Random實作方式(雖然不是你們用的Oracle JDK,但是很像)。
(私語:GNU就是堅持什麼都要開放,有別於什麼都要吉吉吉的公司...)
我們來解說幾個範例有用到的public method:
- Random()
如果你要讓每次的執行結果不一樣,就不要設固定的亂數種子,採用Random()。
public Random()
{
this(System.currentTimeMillis());
}發現好玩的事情了嗎?this()是什麼?
我們之前講過this就是指「Random這個物件」,所以this()在這裡就是用來呼叫「Random(long seed)」。故就算你用no-arg的Random()去創建物件,它其實也是去呼叫Random(long seed),只是只是!!!它幫你傳入的亂數種子是「當下時間」,又因為你每次執行程式的當下時間一定不一樣(可能差幾毫秒鐘),所以乍看之下,我們誤以為Random()創建的物件所得到的亂數是不固定的。
- Random(long seed)
如果看不懂上一段講什麼,那白話文就是
Random random = new Random();等價
Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());結束。
我們來看看那Random(long seed)在做什麼?
public Random(long seed)
{
setSeed(seed);
}seed是Random的private long data field,然後又要去看setSeed(long seed)在做什麼。
- setSeed(long seed)
public synchronized void setSeed(long seed)
{
this.seed = (seed ^ 0x5DEECE66DL) & ((1L << 48) - 1);
haveNextNextGaussian = false;
}我們需要解讀this.seed被設成什麼?
先備知識:
-
用0x開頭表示十六進位的數字。
-
數字以L結尾,代表那個數字的型態是long。
首先((1L << 48) - 1)為2的48次方減1,因為把二進位的1向左移48個位置再補0,轉成十進位,再減1。
再來看0x5DEECE66DL在不同的進位制是多少?
| Binary Digits | 10111011110111011001110011001101101 |
| Decimal Digits | 25214903917 |
| Hexadecimal Digits | 5DEECE66D |
全部查完了,你就能恍然明白
this.seed = (seed ^ 0x5DEECE66DL) & ((1L << 48) - 1);
為什麼要這樣設嗎?
才有鬼!
我們先繼續把這幾個用到的method之間呼叫的關係釐清。
- nextInt()
根據範例輸出發現nextInt()會回傳正整數或負整數,而其中的祕密藏在next()。
public int nextInt()
{
return next(32);
}- nextInt(int n)
根據範例輸出發現nextInt(n)會回傳0到n-1之間的正整數,細看實作:
- 當n<=0程式會丟出例外處理(就是Runtime Error的一種)。
- 當n是2的某次方,就把n倍的next(31)往右移31個位置,其左邊填補原本最左邊的位元值,再回傳。
為什麼(n & -n) == n成真,則n是2的某次方?
我們知道2的某次方在二進位制一定只有一個1和一些0,例如
1000 = 8
反之則其二進位序列至少有兩個1以上,例如
0101 = 5
我們假設n = 0100,則-n = 1011 + 1 = 1100,所以可以得到n & -n = 0100 = n。
觀察其中奧妙就是n的唯一的1的所有左邊位元與其補數透過AND運算子都會變成0,而右邊因為-n是補數加1則會進位成一模一樣;然而若n為0101就沒有右邊的特性。 - 當n是其餘狀況,就回傳next(31)除以n的餘數,並且這個餘數要小於或等於next(31)+n-1,否則就再算一次next(31)...。不管怎樣這個部份一定是回傳0至n-1的數值(因為回傳的是某數除以n的餘數)。
public int nextInt(int n)
{
if (n <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("n must be positive");
if ((n & -n) == n) // i.e., n is a power of 2
return (int) ((n * (long) next(31)) >> 31);
int bits, val;
do
{
bits = next(31);
val = bits % n;
}
while (bits - val + (n - 1) < 0);
return val;
}- next()
我們看見每呼叫一次next()就會更新一次this.seed,其實所有的祕密都藏在next()的實作裡,因為nextInt()或nextInt(int n)都是呼叫next()並把它回傳的值透過固定的方式限制於某個數值以內。
protected synchronized int next(int bits)
{
seed = (seed * 0x5DEECE66DL + 0xBL) & ((1L << 48) - 1);
return (int) (seed >>> (48 - bits));
}- 小結
觀察nextInt(int n)和next()的實作可以很明顯地發現Random是採用導讀提到的線性同餘法(Linear Congruential Formula)來產生新亂數。到這裡我發現若要以數學角度去解釋這種實作方式的位元池夠不夠大(也就是亂數夠不夠亂),以目前的能力來說有困難,因為我們連最基本的Bitwise Operator都不熟悉。權衡之下,與其去借來The Art of Computer Programming囫圇吞下一堆數學符號,不如我們借這次機會熟悉那些運算子。
為了釐清位元運算子的祕密,我們重新兜湊幾個在Random裡面關鍵的method並加上適當的階段性輸出。 範例輸出:
After setSeed(10), seed = (1010 ^ 10111011110111011001110011001101101) & 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 = 10111011110111011001110011001100111
seed = (10111011110111011001110011001100111 * 10111011110111011001110011001101101 + 1011) & 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 = 101110101111110101111010110100101010001111100110
Without setting range for random ouput, next(32) generates value 1111111111111111111111111111111110111010111111010111101011010010
======================
After setSeed(10), seed = (1010 ^ 10111011110111011001110011001101101) & 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 = 10111011110111011001110011001100111
seed = (10111011110111011001110011001100111 * 10111011110111011001110011001101101 + 1011) & 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 = 101110101111110101111010110100101010001111100110
Before shifting, value 10000 * 1011101011111101011110101101001 = 10111010111111010111101011010010000
With setting range (power of 2) for random ouput, nextInt(16) generates value 1011
======================
After setSeed(10), seed = (1010 ^ 10111011110111011001110011001101101) & 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 = 10111011110111011001110011001100111
seed = (10111011110111011001110011001100111 * 10111011110111011001110011001101101 + 1011) & 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 = 101110101111110101111010110100101010001111100110
temporary value = 1011101011111101011110101101001 % 10001 = 11
With setting range for random ouput, nextInt(17) generates value 11
直接看碼:
class GuessRandom {
private static long seed;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long val;
System.out.print("After setSeed(10), ");
setSeed(10);
val = next(32);
System.out.println("Without setting range for random ouput, next(32) generates value " + getBin(val));
System.out.println("======================");
System.out.print("After setSeed(10), ");
setSeed(10);
val = nextInt(16);
System.out.println("With setting range (power of 2) for random ouput, nextInt(16) generates value " + getBin(val));
System.out.println("======================");
System.out.print("After setSeed(10), ");
setSeed(10);
val = nextInt(17);
System.out.println("With setting range for random ouput, nextInt(17) generates value " + getBin(val));
}
public static int nextInt(int n)
{
if (n <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("n must be positive");
if ((n & -n) == n) {// i.e., n is a power of 2
long next_31 = next(31);
System.out.println("Before shifting, value " + getBin(n) + " * " + getBin(next_31) + " = " + getBin(n * (long) next_31));
return (int) ((n * (long) next_31) >> 31);
}
int bits, val;
do
{
bits = next(31);
val = bits % n;
System.out.println("temporary value = " + getBin(bits) + " % " + getBin(n) + " = " + getBin(val));
}
while (bits - val + (n - 1) < 0);
return val;
}
public static int next(int bits)
{
System.out.print("seed = (" + getBin(seed) + " * " + getBin(0x5DEECE66DL) + " + " + getBin(0xBL) + ") & " + getBin((1L << 48) - 1) + " = ");
seed = (seed * 0x5DEECE66DL + 0xBL) & ((1L << 48) - 1);
System.out.println(getBin(seed));
return (int) (seed >>> (48 - bits));
}
public static void setSeed(long seed)
{
System.out.print("seed = (" + getBin(seed) + " ^ " + getBin(0x5DEECE66DL) + ") & " + getBin((1L << 48) - 1) + " = ");
GuessRandom.seed = (seed ^ 0x5DEECE66DL) & ((1L << 48) - 1);
System.out.println(getBin(GuessRandom.seed));
}
public static String getBin(long x){
return Long.toBinaryString(x);
}
}利用Math.random()得到介於1到10之間正整數的作法。
直接看碼:
import java.lang.Math;
public class TestMathRandom {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=10,b=1;
int x = (int) (Math.random() * a ) + b;
System.out.println(x);
}
}解釋一下:
0 <= Math.random() < 1
0 <= Math.random() * a < a
b <= Math.random() * a + b < a + b
然後我們就可以得到介於b(含)到a+b(不含)之間的亂數了。
Donald E. Knuth. 1997. The Art of Computer Programming, Volume 2 (3rd Ed.): Seminumerical Algorithms. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc., Boston, MA, USA.
這裡擺放不知道怎麼分類但是蠻有趣的筆記,歡迎各方英雄好漢相繼補充。
- 消掉句點
直接看碼:
String text = "A string is a sequence of characters. Strings are frequently used in programming. In many
languages, strings are treated as an array of characters, but in Java a string is treated as an
object. This chapter introduces the classes for processing strings.";
text = text.replaceAll("\\.", "");
text = text.toLowerCase();
String[] words = text.split(" ");解釋一下:
replaceAll()的第一個引數要用正規表達式,例如「\\.」是句點的正規表達式,而這整個函式是用來把text裡面所有的句點都消去。當題目的輸入字串是由夾雜句點的句子所構成時就很好用。
正規表達式是什麼?
範例:Mr. Bon口吃(正規版解法)
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class StammerTranslater {
public static void main(String []args){
System.out.print(" Mr. Bon says, ");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = input.nextLine();
s = Pattern.compile("\\A\"").matcher(s).replaceAll("");
s = Pattern.compile("\"\\Z").matcher(s).replaceAll("");
s = Pattern.compile("[a-zA-z]+-").matcher(s).replaceAll("");
System.out.println("Translating...");
System.out.println(s);
}
}正規表達式處理字串很強大,絕對值得一邊Google一邊閱讀推薦的書[1]。
- 你知道ArrayList可以裝東西。
- 再讓你知道Map<String, Integer>可以一邊裝單字一邊裝數量。
- Pane - getChildren().add()
- StackPane - getChildren().add()
- GridPane - add()
- BorderPane - setCenter(), setBottom()
[1] J. E. F. Friedl (2006). Mastering Regular Expressions (3rd ed.). O'Reilly Media, Inc.