OutcrossSeq is a software package for genotyping and imputation in the recombinant populations of outcrossing plants, based on whole-genome low-coverage resequencing data.
You can download the source code and the Demo data here:
https://github.com/xhhuanglab/OutcrossSeq
You can download the Docker container here:
docker run -it -v $PWD:/docker mjchenjojo/outcrossseq:v1.0
#$PWD is the path of your data and perl scripts, you need to put the script and the input vcf file in a folder
The code is implemented in perl (v5.16.3) and can be run from linux shell. To run OutcrossSeq the following libraries and tools should be available:
- R version 3.4.1
- Statistics::Basic module
- Number::Format module
There are three modules in OutcrossSeq.
- "Diploid-Outcrossing" module designed for diploid outcrossing F1 population
- "Double-Cross" module designed for double cross population
- "Autopolyploid Plant" module designed for autopolyploid F1 population.
The input file of "Diploid-Outcrossing" module is variant calling file of two heterozygous parents and all F1 individuals (in VCF format).
See Demo data: demo_diploid.vcf
The input file of "Double-Cross" module is variant calling file of four inbred parents and all offspring individuals.
See Demo data:demo_double.vcf
The input files of "Autopolyploid Plant" module are two separated variant calling files for parents and offsprings, respectively. For parents, variants are called in polyploid mode, for offsprings variants are called in diploid mode.
See Demo data for two hexaploid parents: demo-Parents.vcf and their F1 offsprings demo_autopolyploid.vcf
- For variant calling,we recommend to generate VCF files for each chromosome, which is more convenient to run the code and to tune parameters in following steps.
For details, please see Use cases. "Diploid-Outcrossing" module
cd Diploid-Outcrossing
perl system_diploid_cross.pl 5 100 0.6 0.3 0.35 60 1000 100000 parent1 parent2 demo_diploid
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
100 |
quality threshold we set here as an example, and SNP sites with quality below threshold will be filtered |
0.6 |
miss rate threshold we set here as an example, and missing values greater than the threshold will be filtered |
0.3 |
heterozygosity between 0.3 and (1-0.3) |
0.35 |
start cuttree threshold |
60 |
sample number |
1000 |
min marker number in each window, at least 1000 |
100000 |
window size (<1cM) |
parent1 |
the id of parent1 in vcf file |
parent2 |
the id of parent2 in vcf file |
demo_diploid |
the input file of the vcf file |
perl diploid_cross_step4.pl 5 5 demo
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
first 5 |
start chromosome |
second 5 |
end chromosome |
demo |
output file's name |
"Double-Cross" module
cd Double-Cross
perl system_double_cross.pl 16 17 18 19 5 100 100000 1 6 demo_double
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
16 17 18 19 |
column number of four parents;16—parent1,17—parent2,18—parent3,19—parent4(Caution: 16,17 should be inbred parent1 x parent2 ,the column 18,19 should be inbred parent3 x parent4. If mix up, the result will be wrong) |
5 |
chromosome |
100 |
quality threshold we set here as an example, and SNP sites with quality below threshold will be filtered |
100000 |
window size (<1cM) |
1 |
the first sample order |
6 |
the last sample order |
demo_double |
the input file of the vcf file e |
perl double_cross_step3.pl 5 5 6 100000
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
first 5 |
star of chromosome |
second 5 |
end of chromosome |
6 |
Size of the population |
100000 |
window size (<1cM) |
"Autopolyploid Plant" module
cd Autopolyploid-Plant
perl system_autopolyploid.pl 5 0.08 1 50 0.9 3 100 Parent1 Parent2 demo_autopolyploid-Parents demo_autopolyploid
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
0.08, 1 |
depth range from 0.08 to 1 |
50 |
min SNP marker number of each window |
0.9 |
cuttree |
3 |
select min cuttree marker num |
100 |
quality threshold we set here as an example, and SNP sites with quality below threshold will be filtered |
Parent1 |
the id of parent1 in vcf file) |
Parent2 |
the id of parent2 in vcf file |
demo_autopolyploid-Parents |
the input file of the parents vcf file |
demo_autopolyploid |
the input file of the offsprings vcf file |
perl autopolyploid_step5.pl 5 5
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
first 5 |
start chromosome |
second 5 |
end chromosome |
git clone https://github.com/xhhuanglab/OutcrossSeq.git
cd OutcrossSeq
#list three modules
ls
#autopolyploid_crop diploid_outcrossing_species double_cross_populations readme.md
OutcrossSeq has three modules: "Diploid-Outcrossing", "Double-Cross" and "Autopolyploid Plant". Typically the work includes three steps – sequencing, genotype calling and imputation.
Step1 sequencing: Using Tn5 enzymes for low-cost library construction, hundreds of individuals are then pooled within the same library (each individual with its unique barcode). The pools are sequenced using second-generation sequencing technology and further demultiplexed according to the index tag.
Step2 genotype calling: GATK can be used for genotype calling from whole-genome low-coverage sequencing data.
Step3 imputation: we have three different strategies for different species ("Diploid-Outcrossing" module, "Double-Cross" module and “Autopolyploid Plant” module).
OutcrossSeq works with VCF format files as input. After imputation, the output file is a genotype file that could be directly used for QTL mapping.
"Diploid-Outcrossing" and "Double-Cross" outputs are in bin matrix format, which can be used as the inputs of GACD, MapQTL etc for genetic mapping.
“Autopolyploid Plant” outputs are in SNP matrix format, which can be used as the inputs of fastGWA, EMMAX etc for genetic mapping.
For more details, please check Demo run below.
This module is designed for all diploid outcrossing species. F1 population with about 200 individuals is good enough for a well study using this module.
1:Filter out low-quality SNP sites
cd /OutcrossSeq/diploid_outcrossing_species
perl diploid_cross_Genotype_filter.pl 5 parent1 parent2 100 0.6 demo_diploid 0.3
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
parent1 |
the id of parent1 in vcf file |
parent2 |
the id of parent2 in vcf file |
100 |
quality threshold we set here as an example, and SNP sites with quality below threshold will be filtered |
0.6 |
miss rate threshold we set here as an example, and missing values greater than the threshold will be filtered |
demo_diploid |
the input file of the vcf file |
0.3 |
heterozygosity between 0.3 and (1-0.3) |
2:Calculate kinship of each sample in each windows
perl diploid_cross_step1.pl 100000 1000 F1-chr5.geno 5 0.35
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
100000 |
window size (<1cM) |
1000 |
min marker number in each window, at least 1000 |
F1-chr5.geno |
the input file |
5 |
chromosome |
0.35 |
start cuttree threshold |
3:Clustering in each window
perl diploid_cross_step2.pl 5 60 0.35
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
60 |
sample number |
0.35 |
start cuttree threshold |
Start cuttree threshold can be determine by the evolutionary tree, as example in the figure,you can set a threshold > 0.3. You can randomly select several windows on the chromosome to draw the evolutionary tree to determine the threshold.
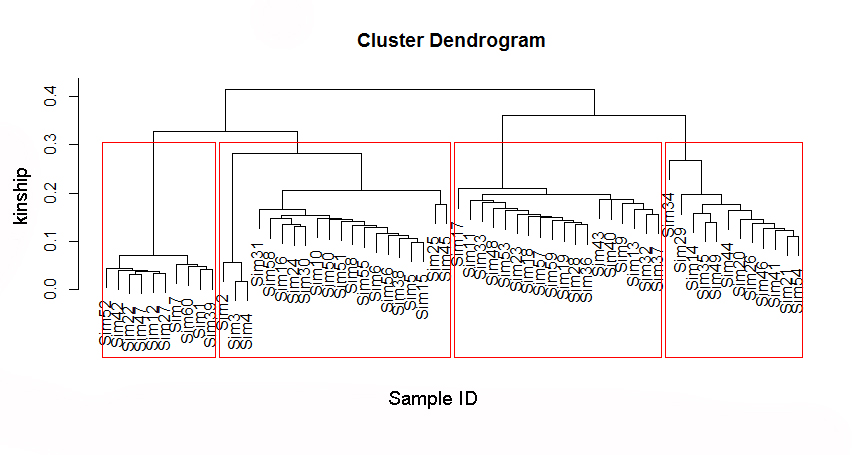
4:Haplotying across the chromosome
In this step, a sample.list is required which records the order of individuals in VCF file.
#less sample.list
Sim1
Sim2
Sim3
Sim4
Sim5
Sim6
Sim7
Sim8
Sim9
Sim10
...
perl diploid_cross_step3.pl 5
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
5:Generate the genotype file
perl diploid_cross_step4.pl 5 5 demo
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
demo |
output file's name |
Optional steps: One may want to check the haplotypes of parents using following command line
perl diploid_cross_Haplotype.pl demo.geno demo_diploid parent1 parent2
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
demo.geno |
the genotype of bin map |
demo_diploid |
the file of vcf file such as demo_diploid.vcf |
parent1 |
the id of parent1 in vcf file |
parent2 |
the id of parent2 in vcf file |
This module is designed for typical Double-Cross population in crop breeding programs, such as rice and maize etc. Population size with 500 individuals is sufficient to carry out a nice study. It can also be applied to other types of populations when the founders are no more than four inbred lines.
1.filter out low-quality low-rate variants and select homozygous variants without missing data and filter the variants that two parents of hybridization have the same mutation and then transform vcf file to genotype file
cd /OutcrossSeq/double_cross_populations
perl double_cross_Genotype_filter.pl demo_double 100 16 17 18 19
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
demo_double |
the input file of the vcf file |
100 |
quality threshold we set here as an example, and SNP sites with quality below threshold will be filtered |
16 17 18 19 |
column number of four parents;16—parent1,17—parent2,18—parent3,19—parent4(Caution: 16,17 should be inbred parent1 x parent2 ,the column 18,19 should be inbred parent3 x parent4. If mix up, the result will be wrong) |
2:Determine the genotype of the first allele
perl double_cross_step1.pl demo_double_parent.geno demo_double_offspring.geno 100000 5 1 6
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
demo_double_parent.geno,demo_double_offspring.geno |
input file |
100000 |
window size (<1cM) |
5 |
chromosome |
1 |
the first sample order |
6 |
the last sample order |
3:Determine the genotype of the second allele
perl double_cross_step2.pl demo_double_parent.geno demo_double_offspring.geno 100000 5 1 6
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
demo_double_parent.geno,demo_double_offspring.geno |
input file |
100000 |
window size (<1cM) |
5 |
chromosome |
1 |
the first sample order |
6 |
the last sample order |
4:Generate the genotype file In this step, a sample.list is required which records the order of individuals in VCF file.
#less sample.list
Sim1
Sim2
Sim3
Sim4
Sim5
Sim6
perl double_cross_step3.pl 5 5 6 100000
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
star of chromosome |
5 |
end of chromosome |
6 |
Size of the population |
100000 |
window size (<1cM) |
This module is designed dedicated for F1 population of autopolyploid or near-autopolyploid plants such as potato and sweet potato etc. A F1</sub Population with about 1000 or more individuals is recommended, for a reasonable practice.
1:Select simplex or double-simplex SNPs
perl autopolyploid_Genotype_filter_step1.pl demo_autopolyploid-Parents 100 0.08 1
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
demo_autopolyploid-Parents |
the input file of the parents vcf file |
100 |
quality threshold we set here as an example, and SNP sites with quality below threshold will be filtered |
0.08,1 |
depth range from 0.08 to 1 |
2:Transform .vcf to .geno file
perl autopolyploid_Genotype_filter_step2.pl 5 demo_autopolyploid Parent1 Parent2
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
demo_autopolyploid |
the input file of the offsprings vcf file |
Parent1 |
the id of parent1 in vcf file |
Parent2 |
the id of parent2 in vcf file |
3:Filter low-quality and error ratio sites This step can be skipped
perl autopolyploid_step1.pl 5 demo_autopolyploid
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
demo_autopolyploid |
the input file of the .geno file |
4:Select relevant sites
perl autopolyploid_step2.pl select-demo_autopolyploid 5 50 0.9 3 100
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| select-demo_autopolyploid | the input file of the select*.geno file |
5 |
chromosome |
50 |
min SNP marker number of each window |
0.9 |
cuttree |
3 |
select min cuttree marker num |
100 |
select max cuttree marker num |
Optimized steps: Then one has to combine all the results together when all runs finished
perl split-select-geno.pl 5 110 50 select-demo_autopolyploid
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
110 |
File lines (Can be obtained by command:wc -l file_name) of select-demo_autopolyploid.geno |
50 |
line number of plit file,be careful this parameter must be a multiple of the min snp number for each window |
select-demo_autopolyploid |
the split file name |
Optimized steps: Then one has to combine all the results together when all runs finished
perl combine_split.pl 5 select-demo_autopolyploid 2
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
5 |
chromosome |
select-demo_autopolyploid |
the split file name |
3 |
Number of split files |
*5:Select mark readsNum * In this step, a sample.list is required which records the order of individuals in VCF file.
#less sample.list
Sim1
Sim2
Sim3
Sim4
Sim5
Sim6
Sim7
Sim8
Sim9
Sim10
...
perl autopolyploid_step3.pl demo_autopolyploid-readsNum.txt R2-select-demo_autopolyploid
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
demo_autopolyploid-readsNum.txt |
input file1 |
R2-select-demo_autopolyploid |
input file2 named R2-select-demo_autopolyploid.txt |
6:Imputation missing SNPs
perl autopolyploid_step4.pl 5 R2-select-demo_autopolyploid-readsNum.txt R2-select-demo_autopolyploid.txt
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
demo_autopolyploid-readsNum.txt |
input file1 |
R2-select-demo_autopolyploid |
input file2 |
7:Merge genotype files
perl autopolyploid_step5.pl 5 5
#because demo data only contains the chromosome 5
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
first 5 |
start chromosome |
second 5 |
end chromosome |
The paper describing OutcrossSeq can be found here:
