A tree is a general structure of recursive nodes. There are many types of trees such as binary tree and balanced tree. Each kind of tree has a different purpose, structure and behaviour. A binary tree stores a collection of comparable items (e.g. numbers) and its structure is sorted so it can be searched quickly to find a single item. (balanced tree is similar in principle). The recursive structure yields a recursive algorithm. A binary tree compares the single searched value to each node.
Searching has O(h) worst-case runtime complexity, where h is the height of the tree. Since s binary search tree with n nodes has a minimum of O(log n) levels, it takes at least O(log n) comparisons to find a particular node.
Insertion of an Element as a left child, we have to traverse all elements and therefore insertion has the worst case complexity of O(n)
Deletion of an element, we again have to traverse all elements to find the child with again has worst case complexity of O(n).
Therefore the Binary Tree time complexity is O(log(n)) for insertion, deletion and searching.
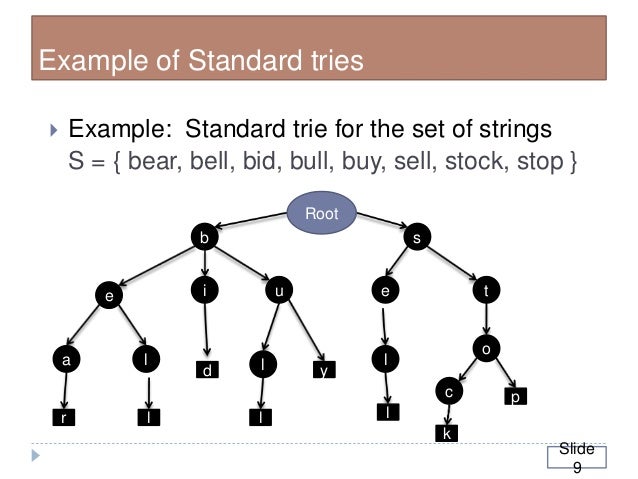
A trie stores sequences of values rather than individual single values in its structure. Each level of recursion says 'what is the value of item 1 of the input list' and does not compare the single searched value to each node as binary trees do. This is an efficient information reTrieval data structure. Using a Trie, search complexities can be brought to optimal limit.
Searching: we can search the key in O(L) time where L represents the length of a single words. This is faster than Binary tree search but we need higher storage capacity. This comes at cost of memeory that is needed.
Insertion: inserting a key into a Trie as an individual Trie node
Delection: use recursion in delete operation to delete the key in a bottom up manner.
Print all words in alphabetical order and efficient prefix search or authocomplete)
Why Trie Data Structure?
- Searching trees in general favor keys which are of fixed size since this leads to efficient storage management.• However in case of applications which are retrieval based and which call for keys varying length, tries provide better options.• Tries are also called as Lexicographic Search trees.
The following picture explains construction of trie using keys given in the example below,
root
/ \ \
t a b
| | |
h n y
| | \ |
e s y e
/ | |
i r w
| | |
r e e
|
r
In the picture, every character is of type trie_node_t. For example, the root is of type trie_node_t, and it’s children a, b and t are filled, all other nodes of root will be NULL. Similarly, “a” at the next level is having only one child (“n”), all other children are NULL. The leaf nodes are in blue.
An article when to use tries for the front-end applications. https://hackernoon.com/practical-data-structures-for-frontend-applications-when-to-use-tries-5428a565eba4
- Trees: Unlike Arrays, Linked Lists, Stack and queues, which are linear data structures, trees are hierarchical data structures.They allow fast lookup, addition and removal of items, and can be used to implement either dynamic sets of items, or lookup tables that allow finding an item by its key (e.g., finding the phone number of a person by name aka dictionary problems).
- Tree Vocabulary: The topmost node is called root of the tree. The elements that are directly under an element are called its children. The element directly above something is called its parent. For example, ‘a’ is a child of ‘f’, and ‘f’ is the parent of ‘a’. Finally, elements with no children are called leaves.
tree
----
j <-- root
/ \
f k
/ \ \
a h z <-- leaves
class Node:
def __init__(self,key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# create root
root = Node(1)
''' following is the tree after above statement
1
/ \
None None'''
root.left = Node(2);
root.right = Node(3);
''' 2 and 3 become left and right children of 1
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
None None None None'''
root.left.left = Node(4);
'''4 becomes left child of 2
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 None None None
/ \
None None''' The lowest common ancestor (LCA) for 2 nodes, N1 and N2, is defined as the the lowest node in the tree, where N1 and N2 are both its decendants.
Nodes 4 and 9 have 2 common ancestors, 1 and 2.
However, 2 is the lower node, so it is their LCA.
Similarly:
- 1 is the LCA of nodes 5 and 6
- 3 is the LCA of nodes 3 and 6.
# Python Program for Lowest Common Ancestor in a Binary Tree
# O(n) solution to find LCS of two given values n1 and n2
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new binary node
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Finds the path from root node to given root of the tree.
# Stores the path in a list path[], returns true if path
# exists otherwise false
def findPath( root, path, k):
# Baes Case
if root is None:
return False
# Store this node is path vector. The node will be
# removed if not in path from root to k
path.append(root.key)
# See if the k is same as root's key
if root.key == k :
return True
# Check if k is found in left or right sub-tree
if ((root.left != None and findPath(root.left, path, k)) or
(root.right!= None and findPath(root.right, path, k))):
return True
# If not present in subtree rooted with root, remove
# root from path and return False
path.pop()
return False
# Returns LCA if node n1 , n2 are present in the given
# binary tre otherwise return -1
def findLCA(root, n1, n2):
# To store paths to n1 and n2 fromthe root
path1 = []
path2 = []
# Find paths from root to n1 and root to n2.
# If either n1 or n2 is not present , return -1
if (not findPath(root, path1, n1) or not findPath(root, path2, n2)):
return -1
# Compare the paths to get the first different value
i = 0
while(i < len(path1) and i < len(path2)):
if path1[i] != path2[i]:
break
i += 1
return path1[i-1] https://medium.com/@codingfreak/binary-tree-interview-questions-and-practice-problems-439df7e5ea1f
-Data Structures: Trees https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oSWTXtMglKE&t=4s