Canvas assignments are interactive pieces of curriculum content that require a submission of work. The work required will be completed on your local machine, so in this lesson, we will go over how to download (also known as forking and cloning), complete, and submit an assignment.
This lesson is your first Canvas assignment! Your task for this assignment is to go through the process of downloading, completing, and submitting. Follow the instructions below for more information.
From the perspective of Canvas, all assignments work in pretty much the same way. An assignment will include some written instructions in Canvas. Based on the provided instructions, you perform some work on your local machine. When your work is complete, you provide a URL pointing to that work as your submission.
However, there are a few types of assignments you'll encounter:
- Labs: These require some amount of code to be written. Labs include tests that will check to see if your code achieves the desired result.
- Code-alongs: These also require code, but will guide you through what needs to be written. There are no tests to pass, but your work still gets submitted.
- Portfolio Projects: For these assignments, you'll be building fully functional applications. Some guidelines and requirements will be provided, but it will be up to you to design and create your own app. These will eventually become the projects you showcase to potential employers!
- Assessments: Assessments can be assigned by an instructor. An assessment will include specific requirements regarding what you need to code, but it will be up to you to ensure you are writing functional code.
- Blog Submissions: Blogs are a required part of our Software Engineering courses. They help to develop your online presence and are a great way to reinforce the concepts you learn. You'll write your blog posts on a different platform, but submit links to them in Canvas.
The majority of assignments will be labs and code-alongs. For each lab and code-along, Canvas displays the written instructions. However, the actual coding work must be completed on your local machine.
The following steps walk through the process of getting the assignment onto your computer. Follow along using this current assignment.
Note: In order to work on and submit assignments, you will need to connect your GitHub account to your Learn.co account. For more information on this, check out this help article
On the assignment's page in Canvas, you'll see two buttons in the upper right corner of the assignment's text. The first is a Fork button. When this button is present, it means this assignment needs to be worked on locally.
Forking is a process where an exact copy is made of a collection of code and files. Clicking the Fork button copies our original version of an assignment over to your personal GitHub account, then redirects you to that new copy.
Forking will allow you to write your own code solution without interfering with the original copy.
Note: In GitHub, there is a Fork button as well. However, this button will not configure your fork with the necessary info for submitting to Canvas, so only use the Fork button in Canvas when working on assignments.
Once an assignment fork has been created, you'll need to download it to your
local machine. To do this, on your personal GitHub fork of the assignment, first
click the Code button. A pop-up will appear that says Clone with HTTPS.
You'll see a URL provided starting with https://....
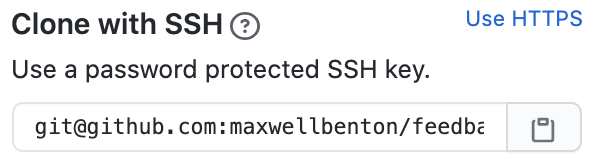
Before doing anything else, make sure to switch from HTTPS to SSH by
clicking the Use SSH link. When clicked, the pop-up will change to display
Clone with SSH. Instead of a URL, you'll see what sort of looks like an
email, starting with [email protected]:.
From here, click the clipboard icon.
Now, open to your terminal and navigate to where you'd like to download the
assignment. For instance, if you followed the local environment setup
instructions, you might have a Flatiron folder with a code sub-folder.
To get to that folder, you'd run the following commands:
cd Flatiron
cd codeYou can always make a new folder with mkdir followed by the name of your
folder, if you want to do so now.
Once you've navigated to where you'd like to store assignments, type
git clone then paste in the copied text from GitHub. It should look
something like this:
git clone [email protected]:<your-user-name>/welcome-completing-assignments.gitPress enter, and you should see a flurry of terminal activity. Once the terminal gives you control to type again, a new folder with the GitHub name of the assignment will be present. Change directory into this folder to access the assignment files.
cd welcome-completing-assignmentsNow, if you've set up VS Code, type code . to open up a text editor window with
access to all of the assignment's files.
Most assignments will have tests that check your work and provide immediate feedback in the terminal. We'll walk through some examples in upcoming lessons.
This assignment has a single test: check to see if you've correctly cloned this assignment to your local machine. If you've followed the steps above, you've completed everything you need to do to pass the test, all that is left to do is run it.
To run an assignment's tests, make sure you're still in the assignment's folder on your local machine, then type the following:
learn testThis command will again cause a flurry of activity in your terminal. After a few moments, you should see the test results printed out. For this assignment, they should look like this:
This assignment
✓ has been correctly cloned to your local environment
1 passing (5ms)Congratulations! You've passed the test.
Note: If you did not receive a passing test, or if your terminal produced some sort of error, walk through the steps in this lesson again and make sure you've followed each one. If you're still receiving errors, we recommend going back to your Welcome course in Canvas and walking through the local environment setup instructions again to ensure everything is set up properly.
When all tests are passing, you can head back to the assignment on Canvas. Refresh the assignment page and you should see that Canvas now registers the assignment as Complete, and you will be ready to move on to the next lesson.
Each assignment will be different and will include instructions on what is
required to complete it. Some labs will have many tests. You can run
learn test as many times as you'd like while working to solve these labs. You
will submit your work to Canvas each time you do, but the assignment will be
marked Incomplete until all tests are passing.
Some assignments do not include tests, but still require some participation on
your part. For these, follow the same process - you will still need to go
through forking, cloning, and running learn test. This command will submit
your fork of the assignment and mark it as complete.
Canvas assignments will also be used for submitting portfolio projects and blogs. For these assignments, the process will be different. For projects, you'll likely be building from scratch rather than forking and cloning. For blogs, you'll be writing your blog posts on some other platform online.
In both cases, you'll need to submit a link to your work on Canvas manually. While viewing the assignment, you should see a Submit Assignment button in the upper-right section of the page.
Clicking this button will bring you to the bottom of the page where you can submit a URL link to your work.
Upon submission you should see confetti appear, indicating that your submission has been accepted.
Note: It is possible to submit lab and code-along assignments this way. However, the assignment will only be marked as submitted, not complete.
You've completed your first assignment! You now know how to work on and submit assignments:
- Click the Fork button on the Canvas assignment
- Once the assignment is forked, clone it down to your local machine
- Complete any required work, then run
learn test - If all tests pass, the assignment will be submitted to Canvas and marked as Complete
Equipped with this knowledge, you are now ready to tackle greater challenges!