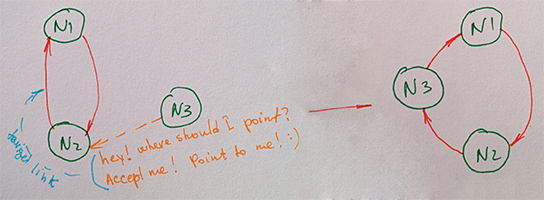Semestral project for the course Distributed Systems and Computing
Program will allow users (nodes) to send messages to each other. All messages must have full ordering (for synchronization use leader or mutual exclusion). All nodes must have at least these functions: send message, login, logout, crash (exit without logout).
The distributed chat will implement a symmetric algorithm with full ordering by using a leader. The chosen Leader Election algorithm is Chang and Roberts for a uni-directional ring of nodes.
The program will be implemented in Python programming language and the nodes will communicate over a REST-ful protocol.
The first node from a topology is pointing to itself and it is forming a one-node ring until it receives a join request from other ring.
A new node will join the ring by knowing the address of any node from the ring by knocking to it. The nodes will accept join requests, will start pointing the knocking node and will send the address of the next node to which the new node will point.
When node A wants to quit the ring it sends a quit request to the neighboring node with its own UID (ip:port) and the UID (ip:port) of it's neighbor.
The neighbor is verifying where it points. If it points to the address of quitting node, it changes its pointer to the neighbor UID received from the request otherwise — it forwards the quit request to the next node.
The system should implement a strategy that recovers the ring structure when a particular node exits unexpectedly.
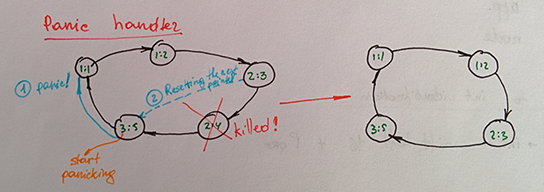
Each node will send a heartbeat signal to its neighbor each 5 seconds. Each node will accept heartbeat signal from its neighbor and will write the timestamp of the heartbeat. If a node is not receiving a heartbeat for 11 seconds (two missed heartbeats + connection tolerance) it starts panicking. Because the ring is unidirectional, the panic will be sent to the next node which will handle it and eventually forward it to the next node.
- The panicking node is sending the panic message to the next node in the topology.
- Nodes that receive this message try to forward it to the next node. In case of failure, we are hitting the dead node, so the node that received the panic handler changes its pointer to the panicking one and discards the message.
After the panic handler finishes its job — we have a fully functional ring again.
Each node is listening on a ip:port. The UID is basically the real binary value of the ip and port. Knowing that the ports are in a 16 bit space and knowing that the ip address represents four 8-bit blocks, I am converting the ip address to its real integer value, shifting left with 16 bits (i.e., multiplying with 2^16) and adding the port value. This is the encoded UID.
The process of decoding the UID to ip:port is similar. The IP address is the UID shifted right with 16 bits. The port number is obtained by masking the UID with 65535, i.e. zeroing all bits except the last 16.
The algorithm assumes that each node has a unique identification UID and all nodes are connected in a ring topology.
When the topology is changed (a node added/removed), the leader election process is triggered. The node that triggers the election is sending an election message with its UID to the next node.
When a process receives an election message it decides:
- If the received UID is greater than the own UID it just forwards the message to the next node and marks itself as a participant to the LE process.
- If the received UID is smaller and the current node is not yet a participant it marks itself as a participant and forwards its UID to the next node.
- If the received UID equal to the self UID then this node starts acting as a leader, marks itself as non-participant and sends elected message to the next node.
When a process receives elected message it marks itself as non participant, records the leader id and forwards elected message to the next node.
When the elected message reaches the newly elected leader, the leader discards that message, and the election is over.
When sending a message we should benefit from the Leader. Each message is initiated and propagated until it reaches the Leader.
When the message reaches the Leader, leader starts persisting them to the next nodes until the message persistence reaches the leader. Now, because the leader is the central authority, we will have full ordering of the messages.
Assuming that you have installed git, python and pip, do the following
$ git clone https://github.com/mishunika/MIE-DSV.git
$ cd MIE-DSV/
$ sudo pip install virtualenv
$ virtualenv flask
$ source flask/bin/activate
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
$ ./app.py src_ip:src_port [target_ip:target_port]