English | 简体中文
PaddlePALM (PArallel Learning from Multi-tasks) is a fast, flexible, extensible and easy-to-use NLP large-scale pretraining and multi-task learning framework. PaddlePALM is a high level framework aiming at fastly developing high-performance NLP models.
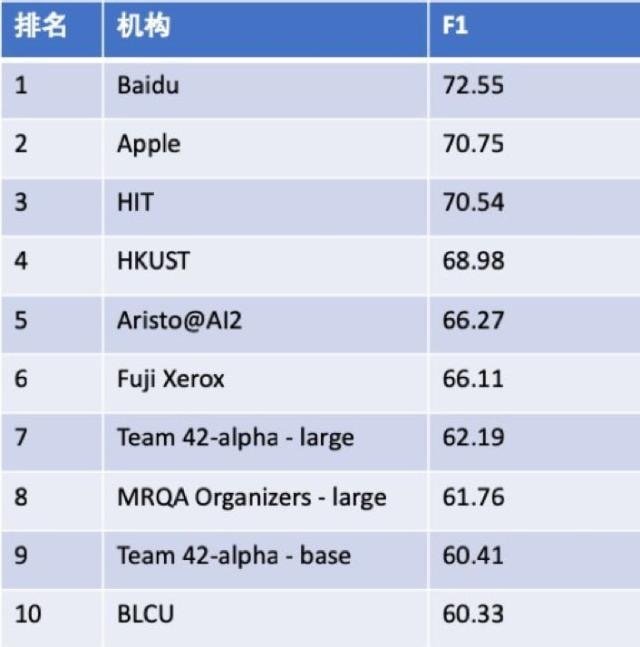
With PaddlePALM, it is easy to achieve effecient exploration of robust learning of NLP models with multiple auxilary tasks. For example, based on PaddlePALM, the produced robust MRC model, D-Net, has achieved the 1st place in EMNLP2019 MRQA track.
MRQA2019 Leaderboard
Beyond the research scope, PaddlePALM has been applied on Baidu Search Engine to seek for more accurate user query understanding and answer mining, which implies the high reliability and performance of PaddlePALM.
- Easy-to-use: with PALM, 8 steps to achieve a typical NLP task. Moreover, all basic components (e.g., the model backbone, dataset reader, task output head, optimizer...) have been decoupled, which allows the replacement of any component to other candidates with quite minor changes of your code.
- Built-in Popular NLP Backbones and Pre-trained models: multiple state-of-the-art general purpose model architectures and pretrained models (e.g., BERT,ERNIE,RoBERTa,...) are built-in.
- Easy to play Multi-task Learning: only one API is needed for jointly training of several tasks with parameters reusement.
- Support train/eval with Multi-GPUs: automatically recognize and adapt to multiple gpus mode to accelerate training and inference.
- Pre-training friendly: self-supervised tasks (e.g., mask language model) are built-in to facilitate pre-training. Easy to train from scratch.
- Easy to Customize: support customized development of any component (e.g, backbone, task head, reader and optimizer) with reusement of pre-defined ones, which gives developers high flexibility and effeciency to adapt for diverse NLP scenes.
You can easily re-produce following competitive results with minor codes, which covers most of NLP tasks such as classification, matching, sequence labeling, reading comprehension, dialogue understanding and so on. More details can be found in examples.
| Dataset
|
chnsenticorp | Quora Question Pairs matching | MSRA-NER (SIGHAN2006) |
CMRC2018 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Metric
|
accuracy
|
f1-score
|
accuracy
|
f1-score
|
f1-score
|
em
|
f1-score
|
|
test
|
test
|
test
|
dev
|
||||
| ERNIE Base | 95.8 | 95.8 | 86.2 | 82.2 | 99.2 | 64.3 | 85.2 |
Architecture Diagram
PaddlePALM is a well-designed high-level NLP framework. You can efficiently achieve supervised learning, unsupervised/self-supervised learning, multi-task learning and transfer learning with minor codes based on PaddlePALM. There are three layers in PaddlePALM architecture, i.e., component layer, trainer layer and high-level trainer layer from bottom to top.
In component layer, PaddlePALM supplies 6 decoupled components to achieve a NLP task. Each component contains rich pre-defined classes and a Base class. Pre-defined classes are aiming at typical NLP tasks, and the base class is to help users develop a new Class (based on pre-defined ones or from the base).
The trainer layer is to establish a computation graph with selected components and do training and predicting. The training strategy, model saving and loading, evaluation and predicting procedures are described in this layer. Noted a trainer can only process one task.
The high-level trainer layer is for complicated learning and inference strategy, e.g., multi-task learning. You can add auxilary tasks to train robust NLP models (improve test set and out-of-domain performance of a model), or jointly training multiple related tasks to gain more performance for each task.
| module | illustration |
|---|---|
| paddlepalm | an open source NLP pretraining and multitask learning framework, built on paddlepaddle. |
| paddlepalm.reader | a collection of elastic task-specific dataset readers. |
| paddlepalm.backbone | a collection of classic NLP representation models, e.g., BERT, ERNIE, RoBERTa. |
| paddlepalm.head | a collection of task-specific output layers. |
| paddlepalm.lr_sched | a collection of learning rate schedualers. |
| paddlepalm.optimizer | a collection of optimizers. |
| paddlepalm.downloader | a download module for pretrained models with configure and vocab files. |
| paddlepalm.Trainer | the core unit to start a single task training/predicting session. A trainer is to build computation graph, manage training and evaluation process, achieve model/checkpoint saving and pretrain_model/checkpoint loading. |
| paddlepalm.MultiHeadTrainer | the core unit to start a multi-task training/predicting session. A MultiHeadTrainer is built based on several Trainers. Beyond the inheritance of Trainer, it additionally achieves model backbone reuse across tasks, trainer sampling for multi-task learning, and multi-head inference for effective evaluation and prediction. |
PaddlePALM support both python2 and python3, linux and windows, CPU and GPU. The preferred way to install PaddlePALM is via pip. Just run following commands in your shell.
pip install paddlepalmgit clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PALM.git
cd PALM && python setup.py install- Python >= 2.7
- cuda >= 9.0
- cudnn >= 7.0
- PaddlePaddle >= 1.7.0 (Please refer to this to install)
We incorporate many pretrained models to initialize model backbone parameters. Training big NLP model, e.g., 12-layer transformers, with pretrained models is practically much more effective than that with randomly initialized parameters. To see all the available pretrained models and download, run following code in python interpreter (input command python in shell):
>>> from paddlepalm import downloader
>>> downloader.ls('pretrain')
Available pretrain items:
=> RoBERTa-zh-base
=> RoBERTa-zh-large
=> ERNIE-v2-en-base
=> ERNIE-v2-en-large
=> XLNet-cased-base
=> XLNet-cased-large
=> ERNIE-v1-zh-base
=> ERNIE-v1-zh-base-max-len-512
=> BERT-en-uncased-large-whole-word-masking
=> BERT-en-cased-large-whole-word-masking
=> BERT-en-uncased-base
=> BERT-en-uncased-large
=> BERT-en-cased-base
=> BERT-en-cased-large
=> BERT-multilingual-uncased-base
=> BERT-multilingual-cased-base
=> BERT-zh-base
>>> downloader.download('pretrain', 'BERT-en-uncased-base', './pretrain_models')
...8 steps to start a typical NLP training task.
- use
paddlepalm.readerto create a reader for dataset loading and input features generation, then callreader.load_datamethod to load your training data. - use
paddlepalm.backboneto create a model backbone to extract text features (e.g., contextual word embedding, sentence embedding). - register your reader with your backbone through
reader.register_withmethod. After this step, your reader is able to yield input features used by backbone. - use
paddlepalm.headto create a task output head. This head can provide task loss for training and predicting results for model inference. - create a task trainer with
paddlepalm.Trainer, then build forward graph with backbone and task head (created in step 2 and 4) throughtrainer.build_forward. - use
paddlepalm.optimizer(andpaddlepalm.lr_schedif is necessary) to create a optimizer, then build backward throughtrainer.build_backward. - fit prepared reader and data (achieved in step 1) to trainer with
trainer.fit_readermethod. - load pretrain model with
trainer.load_pretrain, or load checkpoint withtrainer.load_ckptor nothing to do for training from scratch, then do training withtrainer.train.
For more implementation details, see following demos:
- Sentiment Classification
- Question Pairs matching
- Named Entity Recognition
- SQuAD-like Machine Reading Comprehension.
To run with multi-task learning mode:
- repeatedly create components (i.e., reader, backbone and head) for each task followed with step 1~5 above.
- create empty trainers (each trainer is corresponded to one task) and pass them to create a
MultiHeadTrainer. - build multi-task forward graph with
multi_head_trainer.build_forwardmethod. - use
paddlepalm.optimizer(andpaddlepalm.lr_schedif is necessary) to create a optimizer, then build backward throughmulti_head_trainer.build_backward. - fit all prepared readers and data to multi_head_trainer with
multi_head_trainer.fit_readersmethod. - load pretrain model with
multi_head_trainer.load_pretrain, or load checkpoint withmulti_head_trainer.load_ckptor nothing to do for training from scratch, then do training withmulti_head_trainer.train.
The save/load and predict operations of a multi_head_trainer is the same as a trainer.
For more implementation details with multi_head_trainer, see
To save models/checkpoints and logs during training, just call trainer.set_saver method. More implementation details see this.
To do predict/evaluation after a training stage, just create another three reader, backbone and head instance with phase='predict' (repeat step 1~4 above). Then do predicting with predict method in trainer (no need to create another trainer). More implementation details see this.
If you want to do evaluation during training process, use trainer.train_one_step() instead of trainer.train(). The trainer.train_one_step(batch) achieves to train only one step, thus you can insert evaluation code into any point of training process. The argument batch can be fetched from trainer.get_one_batch.
PaddlePALM also supports multi-head inference, please reference examples/multi-task/joint_predict.py.
If there exists multiple GPUs in your environment, you can control the number and index of these GPUs through the environment variable CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES. For example, if 4 GPUs in your enviroment, indexed with 0,1,2,3, you can run with GPU2 only with following commands
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python run.pyMultiple GPUs should be seperated with ,. For example, running with GPU2 and GPU3, following commands is refered:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2,3 python run.pyOn multi-gpu mode, PaddlePALM will automatically split each batch onto the available cards. For example, if the batch_size is set 64, and there are 4 cards visible for PaddlePALM, then the batch_size in each card is actually 64/4=16. Therefore, when running with multiple cards, you need to ensure that the set batch_size can be divided by the number of cards.
This tutorial is contributed by PaddlePaddle and licensed under the Apache-2.0 license.