In this lab, you will learn how to:
- write and call functions
- compile and code in multiple files
- use
maketo build and format code
This time, the workspace looks a little different:
Makefile- Configuration formake, which you will be using instead ofg++to compile code today.math.cpp- Your code goes here.math.h- Header file formath.cpp, already written for you.main.cpp- Contains main function if you want to run the functions inmath.cpp.
Do not change any files other than math.cpp!
Changes to any other files will create a giant mess for you and will also be ignored by the autograder.
Today, you’ll be using make to compile your code because from now on, our code will involve source code in multiple files.
Don’t compile code for this lab with g++.
Using g++ to compile multiple files by listing all the file names at the same time gets long and tedious.
Using make will save you effort and prevent mistakes.
make is a program that is configured using a file called Makefile, and it makes compiling projects involving multiple source code files easier.
The contents of this Makefile specify what happens when you run the make command.
You can look at the Makefile if you’re curious, but do not make any changes to it.
For this lab, we will have the following make commands.
Note: If you use make somewhere else, you may not have the same commands, so always read the documentation.
make format- Automatically formats your code to meet the style guidelines.make build- Compiles all the program files into a.out.make all- Runs all of the above commands, one by one, in order.make clean- Removes generated files. In this case, a.out.
You’ve spent a few weeks practicing writing code with good style on your own. From now on, you can automatically format your code, which is how most people do it at work.
To do this, simply type make format.
From now on, the autograder will still check your code for good style, but it won’t be worth as many points, since all you have to do is run make format on your code before submitting it.
So far, we have been using // to make a single line a comment.
In C++, you can also make multiline comments using /* to begin the comment and */ to end it.
Anything in between those two will be considered part of the comment.
From now on, we'll have a multiline comment at the beginning of each file. It should contain a line beginning with @file followed by the filename, and a line beginning with @author followed by your name.
You can add other information about what is in the file, but it isn't mandatory for this lab.
When n is positive, x to the nth power is x multiplied by itself n times.
For example, 2 to the 5th power is 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 = 32.
Any number to the 0th power is 1.
Write the power function that does the following given two int inputs x and n:
- If n is negative, return 0.
- Otherwise, return x to the nth power.
power(2, 5) -> 32
power(3, 0) -> 1
power(4, -2) -> 0
The nth root of x is whatever number is equal to x when taken to the nth power.
For example, the 3rd root (also called the cube root) of 8 is 2 because 2 * 2 * 2 = 8.
The integer nth root is the nth root of a number, but anything after the decimal is dropped.
In other words, the integer nth root of x is a number y such that y to the nth power is less than or equal to x and (y + 1) to the nth power is bigger than x.
For example, the integer 3rd root of 10 is 2 because 2 * 2 * 2 = 8 and 8 is less than or equal to 10, and 3 * 3 * 3 = 27 which is bigger than 10.
Write the nth_root function that does the following given two int inputs x and n:
- If n is not positive, return -1.
- If x is negative, return -1.
- Otherwise, return the nth root of x.
nth_root(8, 3) -> 2
nth_root(10, 3) -> 2
nth_root(5, -2) -> -1
nth_root(-3, 4) -> -1
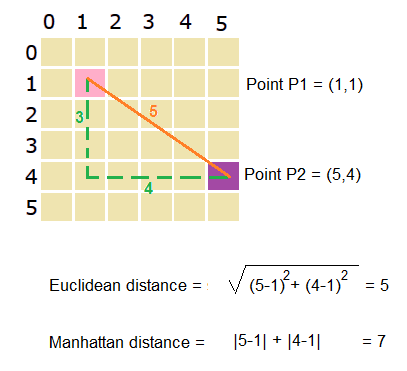
The Manhattan distance between two coordinates (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) can be calculated using the formula |x2 - x1| + |y2 - y1|, where || denotes the absolute value of a number. Think of it as how many steps it takes to go from one point to another on a grid if you're only allowed to go horizontally or vertically.
For example, the horizontal distance between two points (1, 1) and (5, 4) is |5 - 1| = 4, and the vertical distance is |4 - 1| = 3. Put together, we get a Manhattan distance of 4 + 3 = 7.
Write the dist function that does the following given four int inputs x1, y1, x2 and y2:
- Return the Manhattan distance between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2).
dist(1, 1, 5, 4) -> 7
dist(3, -2, 0, 0) -> 5
- (60 points) Programming
- (1 point) TODO comment check
- (2 points) Style check
- (19 points each)
power,nth_rootanddistautograder test cases
- (40 points) Written assignment – see Gradescope for point breakdowns
- Section A: October 12, 11:59pm
- Section B: October 14, 11:59pm
See bit.ly/hwei-cs120-info for all due dates.