本程序一种类似shell命令解释器,shell 是一个用 C 语言编写的程序,它是用户使用 Linux 的桥梁。命令解释器shell提供了一个界面,用户通过这个界面访问操作系统内核的服务。本程序从控制台启动后可以完成用户输入的各种命令。
初次使用请先阅读doc/目录下的YSHELL用户手册!
docs/中所有markdown所引用的图片已经托管至在线的图床服务器,如果您想有良好的阅读体验请保证您的计算机能够联网。
主要特点:
- 友好的界面;
- 支持自定义命令提示符;
- 支持快捷键 或者quit命令 快速结束程序;
- 支持任务后台运行机制;
- 支持输入输出重定向;
- 提供简单的管道系统;
- 提供历史命令查询功能;
运行环境: Linux操作系统(支持64位) ▶ Ubuntu ▶ Debian ▶ Fedora Core/CentOS ▶ SuSE Linux Enterprise Desktop ▶ FreeBSD ▶ Solaris ▶ MacOS
测试环境:
-
Linux ubuntu 5.3.0-40-generic #32-Ubuntu SMP Fri Jan 31 20:24:34 UTC 2020 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
-
Linux ubuntu 4.13.0-36-generic #40~16.04.1-Ubuntu SMP Fri Feb 16 23:25:58 UTC 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
-
Darwin Mac 20.4.0 Darwin Kernel Version 20.4.0: Thu Apr 22 21:46:47 PDT 2021; root:xnu-7195.101.2~1/RELEASE_X86_64 x86_64
代码包文件结构: -codes 代码文件夹 --myshell.c 程序源代码C语言文件 --myshell Linux平台可执行程序(由myshell.c在上述测试环境下编译得到) -docs 文档文件夹 --YSHELL测试报告.md --YSHELL详细设计文档.md --YSHELL需求分析文档.md --YSHELL用户手册.md --YSHELL总结报告.md --README.md
有关常见问题解答、设计文档和测试报告,请参见同目录下doc文件夹。
[toc]
文档更新日期:2021.6.24
文档版本:1.0.0
本程序主要内容为源代码编译,本程序提供测试环境(Linux ubuntu 4.13.0-36-generic #40~16.04.1-Ubuntu SMP Fri Feb 16 23:25:58 UTC 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux)下的可执行文件和C语言源代码文件(均放在 /codes 文件夹下)。如果你运行本程序的操作系统与本测试环境相同,可以跳过本章内容,直接使用可执行文件运行即可。你可以使用一下命令查看你自己的操作系统信息。
uname -a本程序的安装过程主要为C语言源代码的编译,主要过程如下:
-
找到codes/文件夹。
-
右键"在终端中打开"。
-
输入命令:
make Yshell
或者:
gcc Yshell.c -o Yshell
-
如果使用make编译本Yshell源码,您将会看到如下信息:
cc Yshell.c -o Yshell
这代表编译通过。 再次编译,您将会收到如下信息:
make: 'Yshell' is up to date.这代表本次编译与上次编译的源码并没有不同。
如果使用gcc编译本Yshell源码,成功编译时提示符将不会输出信息。
-
如果成功编译,您将会在codes/文件夹下看到一个新的Yshell可执行文件
启动步骤如下:
-
运行本Yshell,您需要在上一步操作之后在同一个文件夹内:
-
右键"在终端中打开"。
-
输入命令:
./Yshell
-
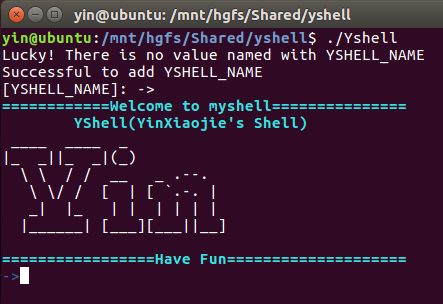
如果程序运行正确,您将会看到如下提示:
Lucky! There is no value named with YSHELL_NAME Successful to add YSHELL_NAME [YSHELL_NAME]: -> ============Welcome to myshell=============== YShell(YinXiaojie's Shell) ____ ____ _ |_ _||_ _|(_) \ \ / / __ _ .--. \ \/ / [ | [ `.-. | _| |_ | | | | | | |______| [___][___||__] =================Have Fun==================== ->
这时候您就可以输入自己的命令并开始与Yshell的愉快之旅了。
本Yshell提供的标准命令提示符为->,如果您想个性化地修改该提示符号,您可以输入:
name=您自己的个性化符号例如:
name=Yin:就可以将->提示符号修改为Yin:。
或者您也可以通过修改变量YSHELL_NAME变量的值的方式来修改您自己的个性化提示符。
例如:
YSHELL_NAME=Yin:您还可以通过printenv命令来查看当前YSHELL_NAME的值。
程序的功能包括:
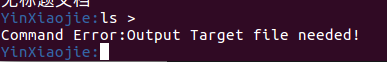
如果命令中不含有输入输出重定向符号< , > 与管道符号 #,那么请直接输入到命令行并运行。
如果该命令无效或者您的计算机并未含有对应的库/包的话,系统将会提示您 当前输入的命令无法被识别:
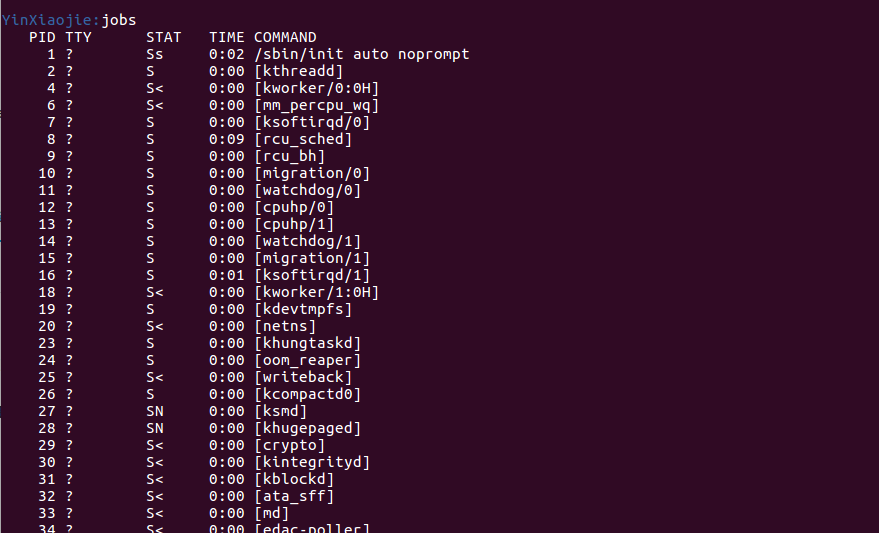
Yshell: Sorry,I have NO idea of your command!需要注意的是,本Shell中的jobs命令已重构,用于查看本计算机的所有进程,功能相当于其他类型Shell的ps ax命令。
< 在本Shell中为输入重定向符号,示例:
cat < in.txt> 在本Shell中为输入重定向符号,示例:
ls > out.txt本Yshell支持 输出1 < 文件 > 输出2 的形式来同时使用输出和输入重定向符号,示例:
cat < out.txt > in.txt本shell支持简单的管道功能,管道命令符号 #,您的命令可以包含一个管道符号, 示例:
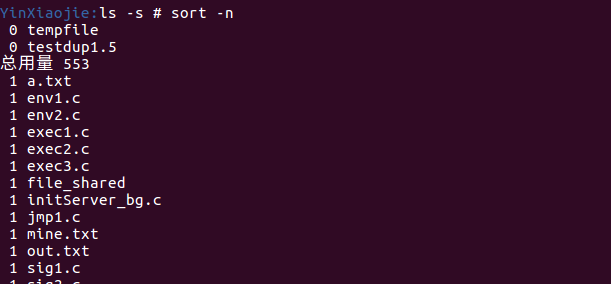
ls -s # sort -n
遗憾的是本Yshell仅支持一个管道符号,含有一个以上的管道符号在执行的时候会提示本Shell功能尚未完善:
Yshell: I'm SORRY this program CAN'T support this command.
But I will improve this part of the function in the future work.
To Be Continued...使用快捷键ctrl+c命令查看您输入的命令历史,最多包含10条。
示例:
->^C
1. cat < ls > a.txt
2. cat < out.txt > a.txt
3. ls -s # sort -n
4. ls -s # sort -n # asda
5. fuck 本Yshell支持两种方式来把任务放到后台执行:
-
方式一:
bg 任务,示例(该示例与对应的示例代码在测试报告中有详尽的示例):->./任务1 ->bg %任务1所对应的pid
-
方式二:
命令 &,更加推荐使用这种方式来执行命令,示例:->ls &
本Yshell支持两种退出方式:
-
快捷键
ctrl-d:->Yshell will close with EOF... ==================GoodBye==================== -
直接输入命令
quit:->quit ==================GoodBye====================
如图所示会有两种不同的提示信息。
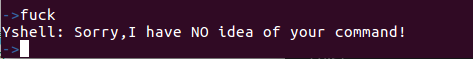
例如输入命令fuck,会提示当前命令无法识别:
->fuck
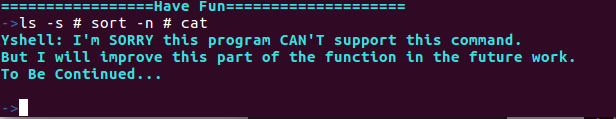
Yshell: Sorry,I have NO idea of your command!当使用类似ls -s # sort -n # a.txt的带有两个管道符号的命令的时候,就不太行了,但是我对于意外情况也提供了处理,Yshell会提示当前的命令现在暂时不能支持,但是在之后的处理当中会进一步完善:
->ls -s # sort -n # cat
Yshell: I'm SORRY this program CAN'T support this command.
But I will improve this part of the function in the future work.
To Be Continued...
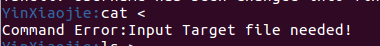
->不提供输出文件/提供的文件无效 的时候,会提示需要目标文件(下图为无效输入的情况,无效输出同理):
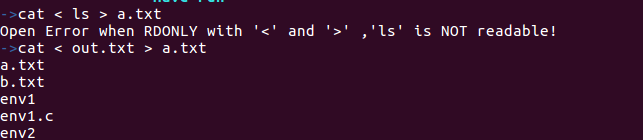
错误示例,输入命令cat < ls > a.txt, 提示ls并非有效可读文件:
->cat < ls > a.txt
Open Error when RDONLY with '<' and '>' ,'ls' is NOT readable!正确示例:
->cat < out.txt > a.txt
a.txt
b.txt
env1| 异常/错误提示 | 错误原因 | 解决方式 |
|---|---|---|
| Failed to add %s | 未能向环境提供局部变量YSHELL_NAME | 手动添加变量YSHELL_NAME到环境变量中 |
| Yshell: bg: no job assigned | 在使用bg命令的时候未能提供有效的任务pid | 供有效的任务pid或创建有效的任务pid |
| Yshell: jobs: incorrect use of jobs | jobs命令使用错误 | 使用ps ax查看当前进程并且正确地使用jobs命令 |
| Yshell: chYshellname:incorrect input of chYshellname | 自定义提示符的时候提供了无效的参数 | 提供有效的参数给YSHELL_NAME |
| Yshell: Sorry,I have NO idea of your command! | 提供了无效的命令或者本shell未安装的命令 | 安装对应的命令或者修改为有效的命令 |
| YShell:Close Error. | 未能正确地关闭已打开的文件 | 停止可能引发已打开文件读写出错的行为或者操作 |
| Command Error:Output Target file needed! | 使用含有 > 命令的时候未提供有效的输出文件参数 | 提供有效的输出文件参数或者修改您的命令 |
| Open Error when O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC with '>' | 未能正确地关闭已打开 > 命令中所指向的文件 | 停止可能引发已打开文件读写出错的行为或者操作 |
| Dup2 Error when STDOUT with '>' ! | > 所包含的dup2指令未能正确执行 | 停止可能引发已打开文件读写出错的行为或者操作 |
| Open Error when RDONLY with '<' and '>' ,'%s' is NOT readable! | 在使用同时包含 <和> 的命令的时候未能提供有效的输出文件 | 停止可能引发已打开文件读写出错的行为或者操作或者提供有效的用于输出文件 |
| Open Error when RDONLY with '#' | 使用含有 # 命令的时候未保证计算机的磁盘正常工作或者系统正常运作,或者恰有有名为"tempfile"的文件被读写 | 更换计算机磁盘或正确修正操作系统或者删除当前文件夹内为"tempfile"的文件 |
| I'm SORRY this program CAN'T support this command. \nBut I will improve this part of the function in the future work. \nTo Be Continued... | 输入了含有多个管道符号#的命令或者输入了本Shell尚未完成的功能的命令 | 减少命令中的管道符号为一个或者等待本Yshell的进一步完善 |
[toc]
docs/中所有markdown所引用的图片已经托管至在线的图床服务器,如果您想有良好的阅读体验请保证您的计算机能够联网。
./Yshell
yin@ubuntu:/mnt/hgfs/Shared/yshell$ ./Yshell
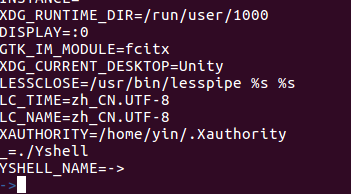
Lucky! There is no value named with YSHELL_NAME
Successful to add YSHELL_NAME
[YSHELL_NAME]: ->
============Welcome to myshell===============
YShell(YinXiaojie's Shell)
____ ____ _
|_ _||_ _|(_)
\ \ / / __ _ .--.
\ \/ / [ | [ `.-. |
_| |_ | | | | | |
|______| [___][___||__]
=================Have Fun====================
->启动Yshell之后,
- 进入
main(),add_envValue()函数成功运行,提示“Lucky! There is no value named with YSHELL_NAME”和“Successful to add YSHELL_NAME” 表示添加YSHELL_NAME到环境变量成功,如上图(如下代码片)。并且提示当前[YSHELL_NAME]: ->。 - 之后调用
welcome()函数,输出欢迎信息并且打印出YIN_banner字符图案。
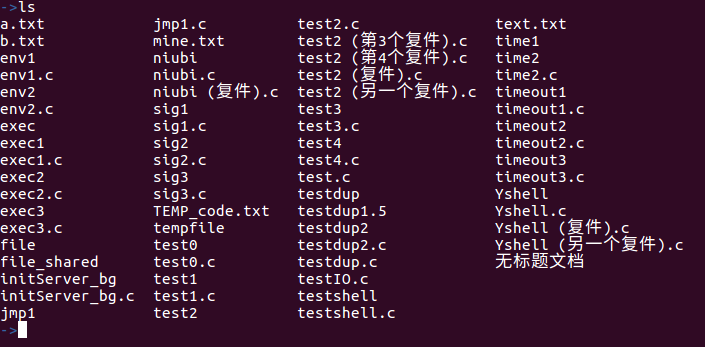
- ls执行测试结果如下:
->ls
a.txt jmp1.c test2.c text.txt
b.txt mine.txt test2 (第3个复件).c time1
env1 niubi test2 (第4个复件).c time2
env1.c niubi.c test2 (复件).c time2.c
env2 niubi (复件).c test2 (另一个复件).c timeout1
env2.c sig1 test3 timeout1.c
exec sig1.c test3.c timeout2
exec1 sig2 test4 timeout2.c
exec1.c sig2.c test4.c timeout3
exec2 sig3 test.c timeout3.c
exec2.c sig3.c testdup Yshell
exec3 TEMP_code.txt testdup1.5 Yshell.c
exec3.c tempfile testdup2 Yshell (复件).c
file test0 testdup2.c Yshell (另一个复件).c
file_shared test0.c testdup.c 无标题文档
initServer_bg test1 testIO.c
initServer_bg.c test1.c testshell
jmp1 test2 testshell.c
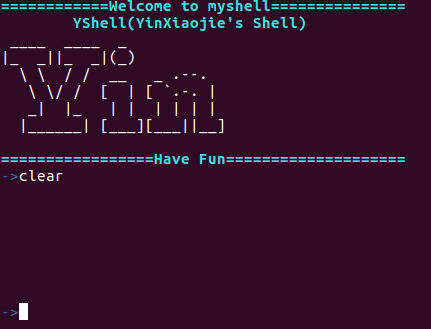
->- clear执行结果如下:
=================Have Fun====================
->clear
->可以看到clear命令执行正常(为了显示命令我把shell页面回滚了)
例如输入命令fuck,会提示当前命令无法识别:
->fuck
Yshell: Sorry,I have NO idea of your command!-
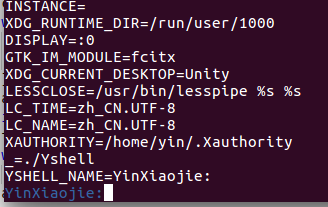
输入命令printenv,打印输出YSHELL_NAME的值为默认的->,说明setenv()的相关函数功能正常:
-
并修改YSHELL_NAME的值, 提示信息:
Yshell: Username has been changed into YinXiaojie:.并且命令行提示符名称修改为了“YinXiaojie:”说明parsecmd()相关的修改变量以及重命名代码正常: -
再次printenv,显示变量YSHELL_NAME已经被修改为了“YinXiaojie:”:
运行命令ls > out.txt并cat out.txt:
YinXiaojie:ls > out.txt
YinXiaojie:cat out.txt
a.txt
b.txt
env1
env1.c
env2
env2.c
exec
exec1
exec1.c
exec2
exec2.cout.txt本不存在,重定向命令在执行的时候就会创建对应的文件,并且将输出重定向到out.txt中:
不提供输入文件/提供的文件无效 的时候,会提示需要目标文件:
执行命令cat < out.txt,输入重定向正常显示对应内容:
YinXiaojie:cat < out.txt
a.txt
b.txt
env1
env1.c
env2
env2.c
exec
exec1
exec1.c
...不提供输出文件/提供的文件无效 的时候,会提示需要目标文件:
- 使用
<和>管道命令时,提供非法参数,错误示例,输入命令cat < ls > a.txt, 提示ls并非有效可读文件:
->cat < ls > a.txt
Open Error when RDONLY with '<' and '>' ,'ls' is NOT readable!- 正确示例:
->cat < out.txt > a.txt
a.txt
b.txt
env1执行命令ls -s # sort -n:ls的结果会传给sort做参数,并且按照行号排序:
但是这个功能并不完善,目前做了单次管道的功能,在多次管道的时候就不管用了:
当使用类似ls -s # sort -n # a.txt的带有两个管道符号的命令的时候,就不太行了,但是我对于意外情况也提供了处理,Yshell会提示当前的命令现在暂时不能支持,但是在之后的处理当中会进一步完善:
->ls -s # sort -n # cat
Yshell: I'm SORRY this program CAN'T support this command.
But I will improve this part of the function in the future work.
To Be Continued...
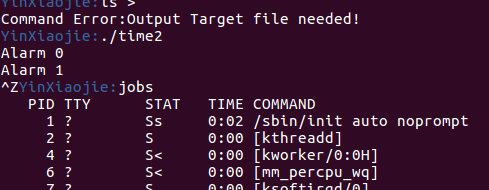
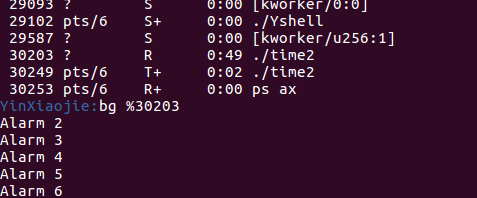
->测试bg命令不是太好测试,我自己写了一个测试程序time2:
yin@ubuntu:/mnt/hgfs/Shared/yshell$ cat time2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
int n = 0;
void timefunc(int sig){
fprintf(stderr, "Alarm %d\n", n++);
signal(SIGALRM, timefunc);
alarm(1);
}
int main()
{
int status;
signal(SIGALRM, timefunc);
alarm(1);
while(1);
return 0;
}
yin@ubuntu:/mnt/hgfs/Shared/yshell$
执行time2,每隔一秒会打印一次Alarm和计数值,之后我们使用ctrl+z挂起time2,使time2在后台暂停,暂时不再输出Alarm:
使用jobs命令查看所有进程找到./time2对应的进程号30203,使用bg %30203使在后台暂停的time2任务改为在后台进行,可以看到./time2继续在后台不断进行并且会打印输出到前台:
该示例在Yshell下与在Ubuntu的shell下执行的输出结果完全一致,说明自己写的bg命令实现了unix自带的bg命令效果。
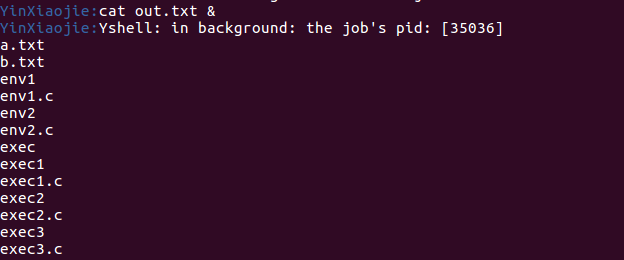
使用命令 cat out.txt & ,运行之后Yshell将任务挂在后台执行,并且立即返回新的提示符,之后cat输出的结果在新的提示符后面显示:
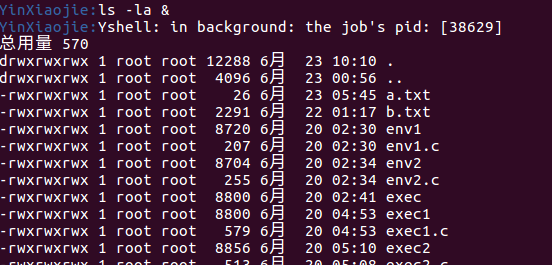
ls命令也是这样:
返回当前计算机的所有进程,结果正常:
使用ctrl+c发送中断信号,信号被注册为查看历史命令的快捷键,最大历史记录条书被MAX_HISTORY所规定,历史记录条数前面还会显示次序:
特定组合键为EOF(ctrl-d),按组合键位退出的时候会提示“Yshell will close with EOF...” ,并且有GoodBye 的字符串友好提示:
直接使用quit退出的时候,只会有GoodBye 的字符串友好提示。
其他测试再次不再赘述,我已经收录了这些测试到本文第三章的部分"三、附录 程序错误列表与解决方式",详情请见下文:
本列表收录了大部分本YShell中可能遇到的错误,并且提供了相应的解决方案。
| 异常/错误提示 | 错误原因 | 解决方式 |
|---|---|---|
| Failed to add %s | 未能向环境提供局部变量YSHELL_NAME | 手动添加变量YSHELL_NAME到环境变量中 |
| Yshell: bg: no job assigned | 在使用bg命令的时候未能提供有效的任务pid | 供有效的任务pid或创建有效的任务pid |
| Yshell: jobs: incorrect use of jobs | jobs命令使用错误 | 使用ps ax查看当前进程并且正确地使用jobs命令 |
| Yshell: chYshellname:incorrect input of chYshellname | 自定义提示符的时候提供了无效的参数 | 提供有效的参数给YSHELL_NAME |
| Yshell: Sorry,I have NO idea of your command! | 提供了无效的命令或者本shell未安装的命令 | 安装对应的命令或者修改为有效的命令 |
| YShell:Close Error. | 未能正确地关闭已打开的文件 | 停止可能引发已打开文件读写出错的行为或者操作 |
| Command Error:Output Target file needed! | 使用含有 > 命令的时候未提供有效的输出文件参数 | 提供有效的输出文件参数或者修改您的命令 |
| Open Error when O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC with '>' | 未能正确地关闭已打开 > 命令中所指向的文件 | 停止可能引发已打开文件读写出错的行为或者操作 |
| Dup2 Error when STDOUT with '>' ! | > 所包含的dup2指令未能正确执行 | 停止可能引发已打开文件读写出错的行为或者操作 |
| Open Error when RDONLY with '<' and '>' ,'%s' is NOT readable! | 在使用同时包含 <和> 的命令的时候未能提供有效的输出文件 | 停止可能引发已打开文件读写出错的行为或者操作或者提供有效的用于输出文件 |
| Open Error when RDONLY with '#' | 使用含有 # 命令的时候未保证计算机的磁盘正常工作或者系统正常运作,或者恰有有名为"tempfile"的文件被读写 | 更换计算机磁盘或正确修正操作系统或者删除当前文件夹内为"tempfile"的文件 |
| I'm SORRY this program CAN'T support this command. \nBut I will improve this part of the function in the future work. \nTo Be Continued... | 输入了含有多个管道符号#的命令或者输入了本Shell尚未完成的功能的命令 | 减少命令中的管道符号为一个或者等待本Yshell的进一步完善 |
docs/中所有markdown所引用的图片已经托管至在线的图床服务器,如果您想有良好的阅读体验请保证您的计算机能够联网。
头文件包含:
/*必要的头文件包含*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>宏定义:
/*宏定义*/
#define MAX_LINE 80 //最大命令长度
#define MAX_HISTORY 10 //最大历史命令存储长度
#define MAX_NAME 30 //最大用户名长度
#define END_COMMAND "exit" //退出命令关键全局变量:
/*全局变量申明*/
char *args[MAX_LINE / 2 + 1]; //接收到的命令字符串
char *args2[MAX_LINE / 2 + 1]; //管道命令 # 右侧的字符串
char *args_in[MAX_LINE / 2 + 1]; //重定向输入的命令字符串
char *args_out[MAX_LINE / 2 + 1]; //重定向输出的命令字符串
enum function{NORMAL,IN,OUT,IN_OUT,PIPE};//功能标识符{正常,<输入重定向命令,>输出重定向命令, #管道命令},通过它进入不同的判断分支
enum function flag = NORMAL; //功能标志
char *usr_name="-> "; //命令提示符
char *usr_name_var="YSHELL_NAME"; //程序向环境提供的变量名
char *usr_name_val="->"; //程序向环境提供的变量内容
char *history[MAX_HISTORY][MAX_LINE / 2 + 1];//历史命令字符串数组
char cmd_buf[MAX_LINE]; //输入命令缓冲
int his_len; //非空的历史命令
int bg=0; //bg命令标志
int chYshellname=0; //修改提示符标志
int func_loc=0; // <, > and # 命令的位置location
int func_in=0; // < 符号在命令中的位置
int func_out=0; // > 符号在命令中的位置/*自己定义的函数*/
void welcome(); //打印欢迎信息,带有颜色
void start(); //接收命令并解析
int getcmd(); //接收命令command
void parsecmd(); //解析命令command
int exec_function(); //执行 普通的命令 和含有<, >, # 的特殊命令
void mybg(pid_t pid); //bg,切换进程到后台
void handle_SIGINT(); //处理ctl+C(SIGINT)信号
void goodbye(); //打印退出信息,带有颜色
void myjobs(); //执行“jobs”对应的功能,查看正在运行的进程
void add_envValue(); //添加YSHELL_NAME为局部环境变量
int itoa(char *des, int i); //转换int到array(为了更加好看的UI)
void append_history(); //添加命令到历史字符串数组功能:
main()函数要实现的 主要功能 为:不断读取用户输入的命令并进行解析与执行,执行函数的时候需要创建子进程,所以整个main()函数的结构是一个死循环for(;;)内嵌创建子进程和处理子进程和父进程的结构。
同时作为总程序的入口,main()函数还要获取环境变量设置命令提示符,注册中断信号,循环执行:打印提示符、等待用户输入、执行用户命令、返回值错误处理。
返回值:
- 0:程序正常运行;
- -1:程序中的进程出错;
实现:
/* 主函数 */
int main()
{
signal(SIGINT,handle_SIGINT);
add_envValue();
his_len =0;
welcome();//欢迎信息
for (;;)
{
bg=0;
chYshellname=0;
func_loc=0;// <, > and # 命令的位置location
func_in=0;// < 符号在命令中的位置
func_out=0;// > 符号在命令中的位置
usr_name=getenv(usr_name_var);
printf("\e[34m%s\e[0m",usr_name);
/* 等待输入要并解析为args */
start();
if (args[0] == NULL) /* input only \n */
continue;
/* 设置 命令历史 */
append_history();
/* fork一个子进程*/
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid<0){
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(pid==0){
int thispid=getpid();//获取子进程pid
signal(SIGINT,SIG_DFL);//默认是终止进程
signal(SIGTSTP,SIG_DFL);//默认是暂停进程
signal(SIGCONT,SIG_DFL);//默认是继续这个进程
if(bg==1){//如果命令需要在后台执行
printf("Yshell: in background: the job's pid: [%d]\n",thispid);
exec_function();
return 0;
}
exec_function();//执行主要命令
break;
}
else if(pid>0){
signal(SIGTSTP,SIG_IGN);//忽视信号
signal(SIGCONT,SIG_DFL);//默认是继续
if(bg==1){//如果命令要在后台执行
signal(SIGCHLD,SIG_IGN);//忽视SIGCHLD信号
}
else{
waitpid(pid,NULL,WUNTRACED);//后台执行的关键代码,必须用WUNTRACED
}
}
else{
perror("Yshell: fork");
break;
}
for (int i = 0; args[i] != NULL; i ++) { /* 释放内存 */
free(args[i]);
args[i] = NULL;
}
}
return 0;
}功能:
打印欢迎信息,提供友好的交互体验;
返回值:
void;
实现:
/* 进入shell时候打印欢迎和友好的提示信息 */
void welcome(){
//如下是欢迎信息
//为了是程序更友好,加入了颜色
//颜色是紫色,背景色与shell相同
printf("\e[1;36m============Welcome to myshell===============\033[0m\n");
printf("\e[1;36m YShell(YinXiaojie's Shell) \e[0m\n");
printf("%s",YIN_banner);
printf("\e[1;36m=================Have Fun====================\e[0m\n");
}功能:
打印退出信息,提供友好的交互体验;
返回值:
void;
实现:
/* 离开shell时候打印goodbye和友好的提示信息 */
void goodbye(){
//为了是程序更友好,加入了颜色
printf("\e[1;36m==================GoodBye====================\e[0m\n");
sleep(1);//暂停1s,看上去视觉效果好一些
exit(0);
}功能:
读取命令输入;
返回值:
- -1 :用户仅输入\n;
- 0 :用户正常输入命令;
实现:
/* 读取命令输入 */
int getcmd(){
flag=NORMAL;
int c;
int len=0;
memset(cmd_buf,0,sizeof(cmd_buf)); /* 初始化buf */
rewind(stdin);
c=getchar();
while(len+1<sizeof(cmd_buf) && c!='\n' && c!=EOF){
cmd_buf[len++]=c;
c=getchar();
}
if(len==0){
if (c=='\n'){ /* 仅输入了 \n */
return -1;
}
printf("\n");
goodbye();
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); /* 退出Yshell的办法1:EOF(ctl-D) */
}
return 0;
}功能:
解析输入的命令,如果有特殊命令< , > ,#的话则打上 标识符flag;
返回值:
void;
实现:
void parsecmd(){
char *p,*q,*t1,*t2; /* p q指针用来记录命令对应 的字符, t1,t2用来记录含有=,即修改提示符时候的名称字符 */
int i=0;
p=q=t1=t2=cmd_buf;
while(*q++!='\0'){
if(*q == '='){ //=代表命令提示符被修改和自定义
t1=t2 =q;
chYshellname=1;
while(*t2++!='\0'){
//只是为了计数而已
continue;
}
args2[0]=(char *) malloc(sizeof(t2 - t1 + 1));
int k=0;
t1++;
while(t1!=t2)
args2[0][k++]=*t1++;
args2[0][k]='\0';
}
if (*q != ' ') /* 在一个词语中 */
continue;
args[i] = (char *) malloc(sizeof(q - p + 1));
int j = 0;
while (*p != ' ')
args[i][j++] = *p++;
args[i++][j] = '\0';
while (*q == ' ') /* 忽视多个空格连在一起的情况 */
*q++;
p = q;
t1 =q;
t2 =q;
}
if (*p != ' ' && *p != '\0') {
args[i] = (char *) malloc(sizeof(q - p + 1));
int j = 0;
while (p != q)
args[i][j++] = *p++;
args[i++][j] = '\0';
}
if (strcmp(args[0],"quit") == 0) {
goodbye();
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); /* 退出Yshell的办法2:输入 quit */
}
else if (strcmp(args[0],"bg")==0){
pid_t pid_bg;
if(args[1]!=NULL){
pid_bg=atoi(args[1]); //用atoi转换,获取pid
}
else{
printf("Yshell: bg: no job assigned\n");
}
char *temp_arg[MAX_LINE / 2 + 1];
for(int y=0;y<i-1;y++){
temp_arg[y]=args[y+1];
args[y]=temp_arg[y];
}
i--;
flag=NORMAL;
mybg(pid_bg);
}
else if(strcmp(args[0],"jobs")==0){//jobs,查看运行的进程
if(args[1]!=NULL){
printf("Yshell: jobs: incorrect use of jobs\n");
}
else
myjobs();
}
else if (chYshellname==1) {
if(args[1]!=NULL){
printf("Yshell: chYshellname:incorrect input of chYshellname\n");
}
else {
printf("Yshell: Username has been changed into %s.\n",args2[0]);
//printf("args2[0]=%s\n",args2[0]);
setenv("YSHELL_NAME",args2[0],1); //修改提示符变量YSHELL_NAME
}
}
if (strcmp(args[i - 1], "&") == 0) { /* bg功能 */
bg = 1;
args[i] = NULL;
free (args[--i]); //必须减掉1,因为&已经被替换了
}
/* 检测 >输入, <输出和 #管道功能*/
int n=0;
for (; args[func_loc] != NULL; ++func_loc )
{
if (strcmp("<", args[func_loc]) == 0)
{
func_in=func_loc;
flag = IN;
i=func_loc;
args[i] = NULL;
continue;
}
if (strcmp(">", args[func_loc]) == 0)
{
func_out=func_loc;
if(flag==NORMAL)
flag = OUT;
else
flag =IN_OUT;
i=func_out;
args[i] = NULL;
continue;
}
else if (strcmp("#", args[func_loc]) == 0)
{
flag = PIPE;
for(n=func_loc+1;n<i;n++){
args2[n-func_loc-1]=args[n];
}
args2[n-func_loc-1]=NULL;
i=func_loc;
args[i] = NULL;
continue;
}
}
for(int in=0;in<=func_in+1;in++){ /* < */
args_in[in]=args[in];
}
if(flag ==IN_OUT){
func_out=func_loc-func_in-2;
for(int out=0;out<=func_loc-func_in-2 ;out++){ /* > */
args_out[out]=args[func_in+3+out];
}
args_out[func_loc]=NULL;
}
else if(flag ==OUT){
for(int out=0;out<=func_out+1;out++) {/* 有时候会有 < file > 两个符号连用的情况 */
args_out[out]=args[out];
}
}
}
功能:
打印欢迎信息,提供友好的交互体验。
返回值:
-
0:正常执行函数并返回;
-
-1:在使用 < 命令的时候发生了错误;
-
-2:在使用 > 命令的时候发生了错误;
-
-3:在同时使用 < 和 > 命令的时候发生了错误;
-
-4:在使用管道命令 # 的时候发生了错误;
实现:
int exec_function(){
int fd=0; /* for output and input ID*/
int fd2=0;
int pid_pipe=0; //pipe 用的子进程
switch(flag)
{
//普通的命令
case NORMAL:
execvp(args[0], args); break;
//带有<的命令
case IN: //printf("Get '<'\n");
if (args_in[func_in+1] == NULL)
{
printf("Command Error:Input Target file needed!\n");
exit(1);
}
fd = open(args_in[func_in+1], O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("Open Error when RDONLY with '<'\n");
return -1;
}
fd2 = dup2(fd,STDIN_FILENO);
if(fd2<0)
{
printf("Dup2 Error when STDIN with '<' \n");
return -1;
}
//执行命令
execvp(args_in[0], args_in);
break;
//带有>的命令
case OUT: //printf("Get '>'\n");
if (args_out[func_out+1] == NULL)
{
//printf("%d",func_out);
printf("Command Error:Output Target file needed!\n");
exit(1);
}
fd = open(args_out[func_out+1], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("Open Error when O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC with '>'\n");
return -2;
}
fd2 = dup2(fd,STDOUT_FILENO);
if(fd2<0)
{
printf("Dup2 Error when STDOUT with '>' !\n");
return -2;
}
//执行命令
execvp(args_out[0], args_out);
break;
//同时有 < > 两种符号的情况
case IN_OUT: //printf("Get '>' and '<' both.\n");
fd = open(args_in[func_in+1], O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("Open Error when RDONLY with '<' and '>' !\n");
return -3;
}
fd2 = dup2(fd,STDIN_FILENO);
if(fd2<0)
{
printf("Dup2 Error when STDIN with '<' and '>' !\n");
return -3;
}
//执行命令
execvp(args_in[0], args_in);
execvp(args_out[0], args_out);
break;
//带有#的管道命令
case PIPE: //printf("Get '#'\n");
pid_pipe=fork();
if(pid_pipe==0)
{
fd2=open("tempfile",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0600);
dup2(fd2,STDOUT_FILENO);
if(fd2<0)
{
printf("Dup2 Error when STDOUT with '#'!\n");
return -4;
}
execvp(args[0], args);
}else{
waitpid(pid_pipe,NULL,0);
fd=open("tempfile",O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("Open Error when RDONLY with '#'\n");
return -4;
}
dup2(fd,STDIN_FILENO);
if(fd2<0)
{
printf("Dup2 Error when STDIN with '#'!\n");
return -4;
}
execvp(args2[0], args2);
}
break;
}
return 0;
}
功能:
bg,切换进程到后台;
返回值:
void;
实现:
/* bg,切换进程到后台 */
void mybg(pid_t pid){
if(kill(pid,SIGCONT)<0){//发送SIGCONT信号
printf("Yshell: bg: no such job\n");//如果有错就打印提示信息
}
else{
waitpid(pid,NULL,WUNTRACED);//和myfg()一样,必须用WUNTRACED
}
}功能:
模拟jobs功能,返回当前计算机所进行的进程;
返回值:
void;
实现:
/* 模拟jobs功能 */
void myjobs(){
//可以使用ps命令来实现查看进程
pid_t pid;
pid=fork();//必须fork,否则会出现myshell退出这种奇怪的bug
if(pid<0){
perror("myshell: fork");
}
else if(pid==0){//子进程
execlp("ps","ps","ax",NULL);//使用ps
// execlp("jobs","jobs",NULL);//使用jobs不可见父类进程创建的job,所以应该用ps
}
else{//父进程
waitpid(pid,NULL,0);
}
}
功能:
给环境变量添加自定义的局部环境变量YSHELL_NAME;
返回值:
void;
实现:
/* 给环境变量添加自定义的局部环境变量YSHELL_NAME */
void add_envValue(){
//Add a value to env
//printf("添加YSHELL_NAME为局部环境变量\n");
usr_name_val = getenv(usr_name_var);
if (!usr_name_val)
{
printf("Lucky! There is no value named with %s\n", usr_name_var);
}
char c1[MAX_NAME] = "YSHELL_NAME";
char c2[MAX_NAME] = "->";
if (setenv(c1,c2,0) == 0) // putenv()仅仅只能起效一次, 所以我改为了setenv()
{
printf("Successful to add %s\n",usr_name_var);
}
else
{
printf("Failed to add %s\n",usr_name_var);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
usr_name_val = getenv(usr_name_var);
if (usr_name_val)
{
printf("[%s]: %s\n", usr_name_var, usr_name_val);
}
//注意:这个新增的环境变量仅仅对这个程序本身有效
//这是因为变量的值不会从子进程(本程序)传播到父进程(Shell)
}功能:
把int转换为des字符串
输入:
- char*des: 用于返回转换之后的字符串;
- int i:待转换的数字;
返回值:
- 0: 转换正常;
- 非零值:转化未成功,int类型未能成功转换为字符串;
实现:
/* 把行标int转换为des字符串 */
int itoa(char *des, int i)
{
char *s = des;
do {
*s++ = i % 10 + '0';
i /= 10;
} while (i > 0);
int res = s - des;
s--;
while (des < s) {
char tmp = *des;
*des = *s;
*s = tmp;
des++;
s--;
}
return res;
}功能:
添加命令到历史字符串数组;
返回值:
void;
实现:
/* 添加命令到历史字符串数组 */
void append_history()
{
int i, j;
if (++his_len > MAX_HISTORY) { /* move history entries to their next */
for (j = 0; history[0][j] != NULL; j++)
free(history[0][j]);
for (i = 0; i < MAX_HISTORY - 1; i++)
for (j = 0; history[i + 1][j] != NULL; j++)
history[i][j] = history[i + 1][j];
} else {
i = his_len - 1;
}
for (j = 0; args[j] != NULL; j++)
history[i][j] = strdup(args[j]);
history[i][j] = NULL;
}