Unified Realtime/API framework for .NET platform and Unity.
MagicOnion is a modern RPC framework for .NET platform that provides bi-directional real-time communications such as SignalR and Socket.io and RPC mechanisms such as WCF and web-based APIs.
This framework is based on gRPC, which is a fast and compact binary network transport for HTTP/2. However, unlike plain gRPC, it treats C# interfaces as a protocol schema, enabling seamless code sharing between C# projects without .proto (Protocol Buffers IDL).
Interfaces are schemas and provide API services, just like the plain C# code
Using the StreamingHub real-time communication service, the server can broadcast data to multiple clients
MagicOnion can be adopted or replaced in the following use cases:
- RPC services such as gRPC, used by Microservices, and WCF, commonly used by WinForms/WPF
- API services such as ASP.NET Core MVC targeting Unity, Xamarin, and Windows clients
- Bi-directional real-time communication such as Socket.io, SignalR, Photon and UNet
MagicOnion uses MessagePack for C# to serialize call arguments and return values. NET primitives and other complex types that can be serialized into MessagePack objects. See MessagePack for C# for details about serialization.
MagicOnion server requires .NET 6.0+.
MagicOnion client supports a wide range of platforms, including .NET Framework 4.6.1 to .NET 7 as well as Unity.
- Server-side (MagicOnion.Server)
- .NET 6.0+
- Client-side (MagicOnion.Client)
- .NET 6+
- .NET Standard 2.1, 2.0
- Unity 2021.3 (LTS) or newer
Start from minimal API(details: Tutorial: Create a minimal web API with ASP.NET Core) so create ASP.NET Core Empty template and Add NuGet package Grpc.AspNetCore and MagicOnion.Server to your project. If you are using the .NET CLI tools to add it, you can run the following command.
dotnet add package Grpc.AspNetCore
dotnet add package MagicOnion.ServerOpen Program.cs and add some configuration to Services and App.
using MagicOnion;
using MagicOnion.Server;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddGrpc(); // Add this line(Grpc.AspNetCore)
builder.Services.AddMagicOnion(); // Add this line(MagicOnion.Server)
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapMagicOnionService(); // Add this line
app.Run();Now you are ready to use MagicOnion on your server project.
MagicOnion provides a Web API-like RPC service and a StreamingHub for real-time communication. This section implements a Web API-like RPC service.
Add an IMyFirstService interface to be shared between the server and the client (namespace should match the project).
using System;
using MagicOnion;
namespace MyApp.Shared
{
// Defines .NET interface as a Server/Client IDL.
// The interface is shared between server and client.
public interface IMyFirstService : IService<IMyFirstService>
{
// The return type must be `UnaryResult<T>` or `UnaryResult`.
UnaryResult<int> SumAsync(int x, int y);
}
}Add a class that implements the interface IMyFirstService. The client calls this class.
using MagicOnion;
using MagicOnion.Server;
using MyApp.Shared;
namespace MyApp.Services;
// Implements RPC service in the server project.
// The implementation class must inherit `ServiceBase<IMyFirstService>` and `IMyFirstService`
public class MyFirstService : ServiceBase<IMyFirstService>, IMyFirstService
{
// `UnaryResult<T>` allows the method to be treated as `async` method.
public async UnaryResult<int> SumAsync(int x, int y)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Received:{x}, {y}");
return x + y;
}
}The service is now defined and implemented. That's it.
Now you can start MagicOnion server as you would a ASP.NET Core project using the F5 key or the dotnet run command.
NOTE: If you want to use MagicOnion client with Unity clients, see also Support for Unity client section.
Create a Console application project and add NuGet package MagicOnion.Client to the project.
Share IMyFirstService interface with the client. Share the interface definition in some way, such as file links, shared libraries, or copy and paste.
In the client code, Create MagicOnionClient client proxy on the shared interface and calls the service transparently.
using Grpc.Net.Client;
using MagicOnion.Client;
using MyApp.Shared;
// Connect to the server using gRPC channel.
var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("https://localhost:5001");
// NOTE: If your project targets non-.NET Standard 2.1, use `Grpc.Core.Channel` class instead.
// var channel = new Channel("localhost", 5001, new SslCredentials());
// Create a proxy to call the server transparently.
var client = MagicOnionClient.Create<IMyFirstService>(channel);
// Call the server-side method using the proxy.
var result = await client.SumAsync(123, 456);
Console.WriteLine($"Result: {result}");MagicOnion is available in four NuGet packages. Please install any of the packages as needed.
NOTE: If you want to use MagicOnion client with Unity clients, see also Support for Unity client section.
The package MagicOnion.Server to implement the server. You need to install this package to implement services on your server.
dotnet add package MagicOnion.ServerThe package MagicOnion.Client to implement the client. To implement the client such as as WPF and Xamarin, you need to install this package.
dotnet add package MagicOnion.ClientThe package MagicOnion.Abstractions provides interfaces and attributes commonly used by servers and clients. To create a class library project which is shared between the servers and the clients, you need to install this package.
dotnet add package MagicOnion.AbstractionsThe package MagicOnion is meta package to implements the role of both server and client.
To implement server-to-server communication such as Microservices, that can be both a server and a client, we recommend to install this package.
dotnet add package MagicOnion- About MagicOnion
- Quick Start
- Installation
- Fundamentals
- Client
- HTTPS (TLS)
- Deployment
- Integrations
- Advanced
- License
A service is a mechanism that provides a request/response API in the style of RPC or Web-API, and is implemented as a Unary call to gRPC. A service can be defined as a C# interface to benefit from the type. This means that it can be observed as a request over HTTP/2.
using System;
using MagicOnion;
namespace MyApp.Shared
{
// Defines .NET interface as a Server/Client IDL.
// The interface is shared between server and client.
public interface IMyFirstService : IService<IMyFirstService>
{
// The return type must be `UnaryResult<T>` or `UnaryResult`.
UnaryResult<int> SumAsync(int x, int y);
// `UnaryResult` does not have a return value like `Task`, `ValueTask`, or `void`.
UnaryResult DoWorkAsync();
}
}using System;
using MagicOnion;
using MagicOnion.Server;
using MyApp.Shared;
namespace MyApp.Services;
// Implements RPC service in the server project.
// The implementation class must inherit `ServiceBase<IMyFirstService>` and `IMyFirstService`
public class MyFirstService : ServiceBase<IMyFirstService>, IMyFirstService
{
// `UnaryResult<T>` allows the method to be treated as `async` method.
public async UnaryResult<int> SumAsync(int x, int y)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Received:{x}, {y}");
return x + y;
}
public async UnaryResult DoWorkAsync()
{
// Something to do ...
}
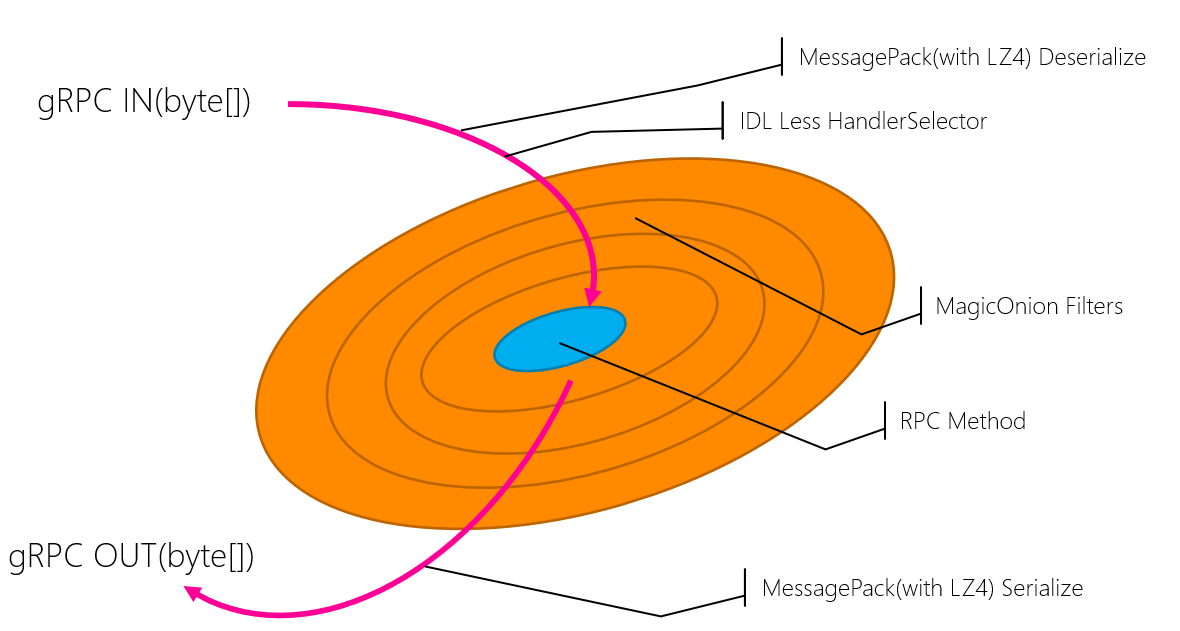
}In MagicOnion, unlike gRPC in general, the body of the request is serialized by MessagePack for sending and receiving.
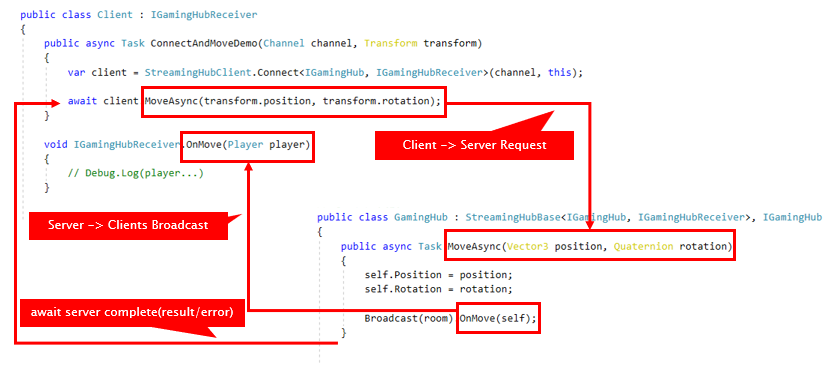
StreamingHub is a fully-typed realtime server <--> client communication framework.
This sample is for Unity(use Vector3, GameObject, etc) but StreamingHub supports .NET Core, too.
// Server -> Client definition
public interface IGamingHubReceiver
{
// The method must have a return type of `void` and can have up to 15 parameters of any type.
void OnJoin(Player player);
void OnLeave(Player player);
void OnMove(Player player);
}
// Client -> Server definition
// implements `IStreamingHub<TSelf, TReceiver>` and share this type between server and client.
public interface IGamingHub : IStreamingHub<IGamingHub, IGamingHubReceiver>
{
// The method must return `ValueTask`, `ValueTask<T>`, `Task` or `Task<T>` and can have up to 15 parameters of any type.
ValueTask<Player[]> JoinAsync(string roomName, string userName, Vector3 position, Quaternion rotation);
ValueTask LeaveAsync();
ValueTask MoveAsync(Vector3 position, Quaternion rotation);
}
// for example, request object by MessagePack.
[MessagePackObject]
public class Player
{
[Key(0)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Key(1)]
public Vector3 Position { get; set; }
[Key(2)]
public Quaternion Rotation { get; set; }
}// Server implementation
// implements : StreamingHubBase<THub, TReceiver>, THub
public class GamingHub : StreamingHubBase<IGamingHub, IGamingHubReceiver>, IGamingHub
{
// this class is instantiated per connected so fields are cache area of connection.
IGroup room;
Player self;
IInMemoryStorage<Player> storage;
public async ValueTask<Player[]> JoinAsync(string roomName, string userName, Vector3 position, Quaternion rotation)
{
self = new Player() { Name = userName, Position = position, Rotation = rotation };
// Group can bundle many connections and it has inmemory-storage so add any type per group.
(room, storage) = await Group.AddAsync(roomName, self);
// Typed Server->Client broadcast.
Broadcast(room).OnJoin(self);
return storage.AllValues.ToArray();
}
public async ValueTask LeaveAsync()
{
await room.RemoveAsync(this.Context);
Broadcast(room).OnLeave(self);
}
public async ValueTask MoveAsync(Vector3 position, Quaternion rotation)
{
self.Position = position;
self.Rotation = rotation;
Broadcast(room).OnMove(self);
}
// You can hook OnConnecting/OnDisconnected by override.
protected override ValueTask OnDisconnected()
{
// on disconnecting, if automatically removed this connection from group.
return ValueTask.CompletedTask;
}
}You can write client like this.
public class GamingHubClient : IGamingHubReceiver
{
Dictionary<string, GameObject> players = new Dictionary<string, GameObject>();
IGamingHub client;
public async ValueTask<GameObject> ConnectAsync(ChannelBase grpcChannel, string roomName, string playerName)
{
this.client = await StreamingHubClient.ConnectAsync<IGamingHub, IGamingHubReceiver>(grpcChannel, this);
var roomPlayers = await client.JoinAsync(roomName, playerName, Vector3.zero, Quaternion.identity);
foreach (var player in roomPlayers)
{
(this as IGamingHubReceiver).OnJoin(player);
}
return players[playerName];
}
// methods send to server.
public ValueTask LeaveAsync()
{
return client.LeaveAsync();
}
public ValueTask MoveAsync(Vector3 position, Quaternion rotation)
{
return client.MoveAsync(position, rotation);
}
// dispose client-connection before channel.ShutDownAsync is important!
public Task DisposeAsync()
{
return client.DisposeAsync();
}
// You can watch connection state, use this for retry etc.
public Task WaitForDisconnect()
{
return client.WaitForDisconnect();
}
// Receivers of message from server.
void IGamingHubReceiver.OnJoin(Player player)
{
Debug.Log("Join Player:" + player.Name);
var cube = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube);
cube.name = player.Name;
cube.transform.SetPositionAndRotation(player.Position, player.Rotation);
players[player.Name] = cube;
}
void IGamingHubReceiver.OnLeave(Player player)
{
Debug.Log("Leave Player:" + player.Name);
if (players.TryGetValue(player.Name, out var cube))
{
GameObject.Destroy(cube);
}
}
void IGamingHubReceiver.OnMove(Player player)
{
Debug.Log("Move Player:" + player.Name);
if (players.TryGetValue(player.Name, out var cube))
{
cube.transform.SetPositionAndRotation(player.Position, player.Rotation);
}
}
}MagicOnion filter is powerful feature to hook before-after invoke. It is useful than gRPC server interceptor.
// You can attach per class/method like [SampleFilter]
// for StreamingHub methods, implement StreamingHubFilterAttribute instead.
public class SampleFilterAttribute : MagicOnionFilterAttribute
{
public override async ValueTask Invoke(ServiceContext context, Func<ServiceContext, ValueTask> next)
{
try
{
/* on before */
await next(context); // next
/* on after */
}
catch
{
/* on exception */
throw;
}
finally
{
/* on finally */
}
}
}Here is example of what kind of filter can be stacked.
MagicOnion also provides an API for filters that is very similar to filter on ASP.NET Core MVC. These APIs support flexible filter implementations.
IMagicOnionServiceFilterinterfaceIStreamingHubFilterinterfaceIMagicOnionFilterFactory<T>interfaceIMagicOnionOrderedFilterinterface
Filters can be ordered and they are executed in the following order:
[Ordered Filters] -> [Global Filters] -> [Class Filters] -> [Method Filters]
Unordered filters are treated as last (int.MaxValue) and executed in the order in which they are added.
Filters that apply to the application globally can be added at GlobalFilters of MagicOnionOptions.
services.AddMagicOnion(options =>
{
options.GlobalFilters.Add<MyServiceFilter>();
options.GlobalStreamingHubFilters.Add<MyHubFilter>();
});MagicOnion filters supports Dependency Injection. There are two ways to activate a filter by using FromTypeFilter, FromServiceFitler or by using IMagicOnionFilterFactory.
The following is an example of how to use FromTypeFilter, FromServiceFitler.
public class MyServiceFilterAttribute : MagicOnionFilterAttribute
{
private readonly ILogger _logger;
// the `logger` parameter will be injected at instantiating.
public MyServiceFilterAttribute(ILogger<MyServiceFilterAttribute> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public override async ValueTask Invoke(ServiceContext context, Func<ServiceContext, ValueTask> next)
{
_logger.LogInformation($"MyServiceFilter Begin: {context.Path}");
await next(context);
_logger.LogInformation($"MyServiceFilter End: {context.Path}");
}
}Register filters using attributes with constructor injection(you can use [FromTypeFilter] and [FromServiceFilter]).
[FromTypeFilter(typeof(MyFilterAttribute))]
public class MyService : ServiceBase<IMyService>, IMyService
{
// The filter will instantiate from type.
[FromTypeFilter(typeof(MySecondFilterAttribute))]
public UnaryResult<int> Foo()
{
return UnaryResult(0);
}
// The filter will instantiate from type with some arguments. if the arguments are missing, it will be obtained from `IServiceProvider`
[FromTypeFilter(typeof(MyThirdFilterAttribute), Arguments = new object[] { "foo", 987654 })]
public UnaryResult<int> Bar()
{
return UnaryResult(0);
}
// The filter instance will be provided via `IServiceProvider`.
[FromServiceFilter(typeof(MyFourthFilterAttribute))]
public UnaryResult<int> Baz()
{
return UnaryResult(0);
}
}The following is an example of how to use IMagicOnionFilterFactory<T>.
This is a clean way of writing when using DI while still having parameters for the attributes.
public class MyServiceFilterAttribute : Attribute, IMagicOnionFilterFactory<IMagicOnionServiceFilter>, IMagicOnionOrderedFilter
{
readonly string label;
public int Order { get; set; } = int.MaxValue;
public MyServiceFilterAttribute(string label)
{
this.label = label;
}
public IMagicOnionServiceFilter CreateInstance(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
=> new MyServiceFilter(serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<ILogger<MyServiceFilterAttribute>>());
class MyServiceFilter : IMagicOnionServiceFilter
{
readonly string label;
readonly ILogger logger;
public MyServiceFilter(string label, ILogger<MyServiceFilterAttribute> logger)
{
this.label = label;
this.logger = logger;
}
public async ValueTask Invoke(ServiceContext context, Func<ServiceContext, ValueTask> next)
{
logger.LogInformation($"[{label}] MyServiceFilter Begin: {context.Path}");
await next(context);
logger.LogInformation($"[{label}] MyServiceFilter End: {context.Path}");
}
}
}[MyServiceFilter("Class")]
public class MyService : ServiceBase<IMyService>, IMyService
{
[MyServiceFilter("Method")]
public UnaryResult<int> Foo()
{
return UnaryResult(0);
}
}The following interfaces are provided for filter extensions. These interfaces are similar to ASP.NET Core MVC filter mechanism.
IMagicOnionFilterFactory<T>IMagicOnionOrderedFilterIMagicOnionServiceFilterIStreamingHubFilter
MagicOnionFilterAttributes and StreamingHubFilterAttribute implement these interfaces for easy use. You can use these interfaces for more flexible implementation.
MagicOnion client-filter is a powerful feature to hook before-after invoke. It is useful than gRPC client interceptor.
Currently only supports on Unary.
// you can attach in MagicOnionClient.Create.
var client = MagicOnionClient.Create<ICalcService>(channel, new IClientFilter[]
{
new LoggingFilter(),
new AppendHeaderFilter(),
new RetryFilter()
});You can create custom client-filter by implements IClientFilter.SendAsync.
public class IDemoFilter : IClientFilter
{
public async ValueTask<ResponseContext> SendAsync(RequestContext context, Func<RequestContext, ValueTask<ResponseContext>> next)
{
try
{
/* Before Request, context.MethodPath/CallOptions/Items, etc */
var response = await next(context); /* Call next filter or method body */
/* After Request, response.GetStatus/GetTrailers/GetResponseAs<T>, etc */
return response;
}
catch (RpcException ex)
{
/* Get gRPC Error Response */
throw;
}
catch (OperationCanceledException ex)
{
/* If canceled */
throw;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
/* Other Exception */
throw;
}
finally
{
/* Common Finalize */
}
}
}Here is the sample filters, you can imagine what you can do.
public class AppendHeaderFilter : IClientFilter
{
public async ValueTask<ResponseContext> SendAsync(RequestContext context, Func<RequestContext, ValueTask<ResponseContext>> next)
{
// add the common header(like authentication).
var header = context.CallOptions.Headers;
if (!header.Any(x => x.Key == "x-foo"))
{
header.Add("x-foo", "abcdefg");
header.Add("x-bar", "hijklmn");
}
return await next(context);
}
}
public class LoggingFilter : IClientFilter
{
public async ValueTask<ResponseContext> SendAsync(RequestContext context, Func<RequestContext, ValueTask<ResponseContext>> next)
{
Console.WriteLine("Request Begin:" + context.MethodPath); // Debug.Log in Unity.
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var response = await next(context);
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("Request Completed:" + context.MethodPath + ", Elapsed:" + sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds + "ms");
return response;
}
}
public class ResponseHandlingFilter : IClientFilter
{
public async ValueTask<ResponseContext> SendAsync(RequestContext context, Func<RequestContext, ValueTask<ResponseContext>> next)
{
var response = await next(context);
if (context.MethodPath == "ICalc/Sum")
{
// You can cast response type.
var sumResult = await response.GetResponseAs<int>();
Console.WriteLine("Called Sum, Result:" + sumResult);
}
return response;
}
}
public class MockRequestFilter : IClientFilter
{
public async ValueTask<ResponseContext> SendAsync(RequestContext context, Func<RequestContext, ValueTask<ResponseContext>> next)
{
if (context.MethodPath == "ICalc/Sum")
{
// don't call next, return mock result.
return new ResponseContext<int>(9999);
}
return await next(context);
}
}
public class RetryFilter : IClientFilter
{
public async ValueTask<ResponseContext> SendAsync(RequestContext context, Func<RequestContext, ValueTask<ResponseContext>> next)
{
Exception lastException = null;
var retryCount = 0;
while (retryCount != 3)
{
try
{
// using same CallOptions so be careful to add duplicate headers or etc.
return await next(context);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
lastException = ex;
}
retryCount++;
}
throw new Exception("Retry failed", lastException);
}
}Service/StreamingHub's method or MagicOnionFilter can access this.Context it is
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
ConcurrentDictionary<string, object> Items |
Object storage per request/connection. |
Guid ContextId |
Unique ID per request(Service)/connection(StreamingHub). |
DateTime Timestamp |
Timestamp that request/connection is started time. |
Type ServiceType |
Invoked Class. |
MethodInfo MethodInfo |
Invoked Method. |
| `ILookup<Type, Attribute> AttributeLookup | Cached Attributes that merged both service and method. |
ServerCallContext CallContext |
Raw gRPC Context. |
MessagePackSerializerOptions SerializerOptions |
Using MessagePack serializer options. |
IServiceProvider ServiceProvider |
Get the service provider. |
Items is useful, for example authentication filter add UserId to Items and take out from service method.
If using StreamingHub, ServiceContext means per connected context so
Itemsis not per method invoke.StreamingHubContext.Itemssupports per streaming hub method request but currently can not take from streaming hub method(only use in StreamingHubFilter). Issue:#67, it will fix.
MagicOnion supports get current context globally like HttpContext.Current. ServiceContext.Current can get it but it requires MagicOnionOptions.EnableCurrentContext = true, default is false.
Lifecycle image of ServiceBase
gRPC In(
var context = new ServiceContext();
Filter.Invoke(context,
var service = new ServiceImpl();
service.ServiceContext = context;
service.MethodInvoke(
/* method impl */
)
)
)
Lifecycle image of StreamingHub(StreamingHub is inherited from ServiceBase)
gRPC In(
var context = new ServiceContext();
Filter.Invoke(context,
var hub = new StreamingHubImpl();
hub.ServiceContext = context;
hub.Connect(
while (connecting) {
Streaming In(
var streamingHubContext = new StreamingHubContext(context);
StreamingHubFilter.Invoke(streamingHubContext,
hub.MethodInvoke(
/* method impl */
)
)
)
}
)
)
)
StreamingHub instance is shared while connecting so StreamingHub's field can use cache area of connection.
If you are return custom status code from server to client, you can use throw new ReturnStatusException.
public Task SendMessageAsync(string message)
{
if (message.Contains("foo"))
{
//
throw new ReturnStatusException((Grpc.Core.StatusCode)99, "invalid");
}
// ....Client can receive exception as gRPC's RpcException. If performance centric to avoid exception throw, you can use raw gRPC CallContext.Status(ServiceContext.CallContext.Status) and set status directly.
MagicOnion's engine catched exception(except ReturnStatusException), set StatusCode.Unknown and client received gRPC's RpcException. If MagicOnionOption.IsReturnExceptionStackTraceInErrorDetail is true, client can receive StackTrace of server exception, it is very useful for debugging but has critical issue about security so should only to enable debug build.
StreamingHub's broadcast system is called Group. It can get from StreamingHub impl method, this.Group(this.Group type is HubGroupRepository, not IGroup).
Current connection can add to group by this.Group.AddAsync(string groupName), return value(IGroup) is joined group broadcaster so cache to field. It is enable per connection(if disconnected, automatically leaved from group). If you want to use some restriction, you can use TryAddAsync(string groupName, int incluciveLimitCount, bool createIfEmpty).
IGroup can pass to StreamingHub.Broadcast, BroadcastExceptSelf, BroadcastExcept and calls client proxy.
public class ChatHub : StreamingHubBase<IChatHub, IMessageReceiver>, IChatHub
{
string userName;
IGroup room;
public async ValueTask JoinAsync(string userName, string roomName)
{
this.userName = userName;
this.room = await Group.AddAsync(roomName);
}
public async ValueTask SendMessageAsync(string message)
{
Broadcast(room).OnReceiveMessage(userName, message);
}
}GroupRepository is created per StreamingHub type
If you want to create ServerSide loop and broadcast out of StreamingHub, you can pass Broadcast(room) result but it is unnatural, I'll add support kit of create server-side loop
Group has in-memory storage, it can store extra data to group member. It can set Group.AddAsync(string groupName, TStorage data) instead of standard AddAsync.
Data is can get from group.GetInMemoryStorage<T> and can invoke AllValues, Set(Guid connectionId, T Value), Get(Guid connectionId).
StreamingHub's ConnectionId is ServiceContext.ContextId
Default MagicOnion's group is inmemory and using ImmutableArrayGroup. This group implementation is tuned for small room, not enter/leave frequently. If large room and enter/leave frequently design, you can use ConcurrentDictionaryGroup. It can configure by GroupConfigurationAttribute or MagicOnionOptions.DefaultGroupRepositoryFactory.
// use ***GroupRepositoryFactory type.
[GroupConfiguration(typeof(ConcurrentDictionaryGroupRepositoryFactory))]
public class ChatHub : StreamingHubBase<IChatHub, IMessageReceiver>, IChatHub
{
// ...
}MagicOnion has distribute system called redis-backplane for group broadcast.
dotnet add package MagicOnion.Server.Redisservices.AddMagicOnion()
.UseRedisGroupRepository(options =>
{
options.ConnectionMultiplexer = ConnectionMultiplexer.Connect("localhost:6379");
});
// If you want to use Redis backplane by default, you can specify `registerAsDefault: true`.// Use Redis as backplane
[GroupConfiguration(typeof(RedisGroupRepositoryFactory))]
public class ...
{
}Like Dependency Injection on ASP.NET Core MVC, MagicOnion also supports DI to services and hubs.
public class MyFirstService : ServiceBase<IMyFirstService>, IMyFirstService
{
IOptions<MyConfig> config;
ILogger<MyFirstService> logger;
public MyFirstService(IOptions<MyConfig> config, ILogger<MyFirstService> logger)
{
this.config = config;
this.logger = logger;
}
// ...
}The recommended structure for a solution using MagicOnion is as follows:
- Client (WPF, Console, etc ...)
- Server (ASP.NET Core Application)
- Shared (Class library)
The Shared project is a library project with interface definitions like Service or Hub and types of requests/responses, shared between the Server and Client.
When developing using Unity, recommended way is use UPM local file reference. For more details on package referencing, please refer to the document of the sample project.
MagicOnion supports Unity, NativeAOT, and other platforms that require pre-generated client code with Source Generator (MagicOnion.Client.SourceGenerator).
MagicOnion.Client.SourceGenerator is shipped with MagicOnion.Client package. This means that you no longer need to the install generator tool (moc) and setup additional build steps.
- Unity 2021.3.0f1 or later
- .NET 6 or later
- Visual Studio 2022 version 17.2 or later
- Rider 2023.1 or later
Define a partial class with any name of your choosing within the application. Mark it with the MagicOnionClientGeneration attribute, and specify any service type found within the assembly where you want to search for the service interface.
For example, if the MyApp.Shared assembly contains MyApp.Shared.Services.IGreeterService and MyApp.Shared.Hubs.IChatHub, specify one of them.
using MagicOnion.Client;
[MagicOnionClientGeneration(typeof(MyApp.Shared.Services.IGreeterService))]
partial class MagicOnionGeneratedClientInitializer {}Next, configure MessagePack to use the generated MessagePack Resolver. This is the same as when using the legacy MagicOnion.Generator.
#if UNITY_2019_4_OR_NEWER
[UnityEngine.RuntimeInitializeOnLoadMethod(UnityEngine.RuntimeInitializeLoadType.BeforeSceneLoad)]
#elif NET5_0_OR_GREATER
[System.Runtime.CompilerServices.ModuleInitializer]
#endif
static void RegisterResolvers()
{
StaticCompositeResolver.Instance.Register(
// Add: Use MessagePack formatter resolver generated by the source generator.
MagicOnionGeneratedClientInitializer.Resolver,
MessagePack.Resolvers.GeneratedResolver.Instance,
BuiltinResolver.Instance,
PrimitiveObjectResolver.Instance
);
MessagePackSerializer.DefaultOptions = MessagePackSerializer.DefaultOptions
.WithResolver(StaticCompositeResolver.Instance);
}You can specify options in the named constructor of the attribute.
DisableAutoRegistration: Sets whether to disable automatically callingRegisterduring start-up. (Automatic registration requires .NET 5+ or Unity)MessagePackFormatterNamespace: Sets the namespace of pre-generated MessagePackFormatters. The default value isMessagePack.Formatters.Serializer: Sets the serializer used for message serialization. The default value isGenerateSerializerType.MessagePack.
MagicOnion supports from Unity version 2021.3.0f1 (LTS) and above, which is available for .NET 4.x runtime and C# 9 or latest.
Using MagicOnion with Unity client requires the following things:
- gRPC library
- MessagePack for C#
- MagicOnion.Client for Unity
There are two ways to use the gRPC library in Unity:
- Using YetAnotherHttpHandler and grpc-dotnet (recommended)
- Using gRPC's C-core (not recommended)
Since the maintenance of the C-core based library has ended in the gRPC project, we recommend using YetAnotherHttpHandler . Please refer to the README of YetAnotherHttpHandler for installation instructions.
If you are using the C-core gRPC library, please define MAGICONION_USE_GRPC_CCORE symbol in "Scripting Define Symbols".
MessagePack for C# is not included in MagicOnion package. You need to download and install separately.
See MessagePack for C# installation for Unity for details.
There are two methods to install the MagicOnion.Client package:
- Using the Unity package manager from git (recommended)
- Using a .unitypackage.
To install using the Unity package manager, please specify the following URL in "Add package from git URL...". Specify the version tag as needed.
https://github.com/Cysharp/MagicOnion.git?path=src/MagicOnion.Client.Unity/Assets/Scripts/MagicOnion#{Version}
Note
Please replace {Version} with the version number you want to install (e.g. 6.0.1).
MagicOnion.Client.Unity.package is available for download from Releases page of this repository.
The package contains the code to use MagicOnion with Unity. It consists of several extensions for Unity in addition to MagicOnion.Client NuGet package.
If your project uses IL2CPP as a scripting backend, additional setup will be required. See Ahead-of-Time compilation support with Source Generator section for details.
Wraps gRPC channels and provides a mechanism to manage them with Unity's lifecycle. This prevents your application and the Unity Editor from freezing by releasing channels and StreamingHub in one place.
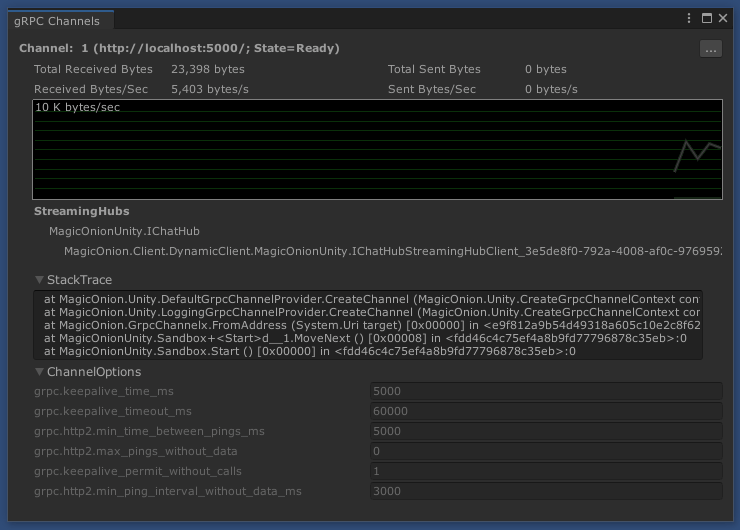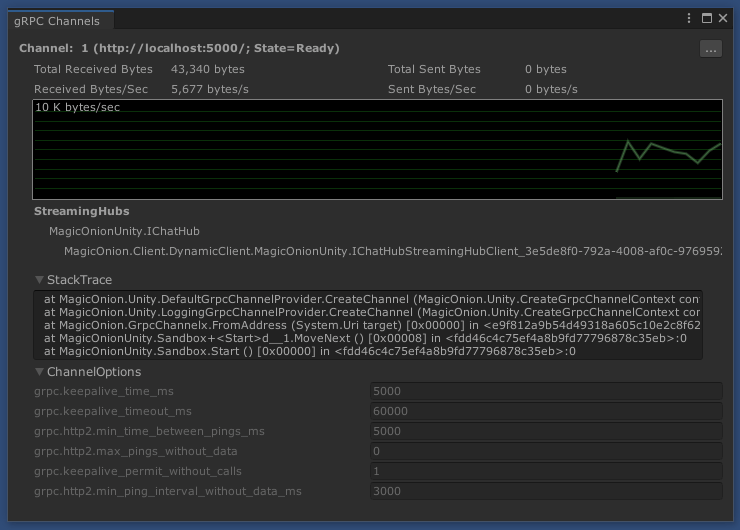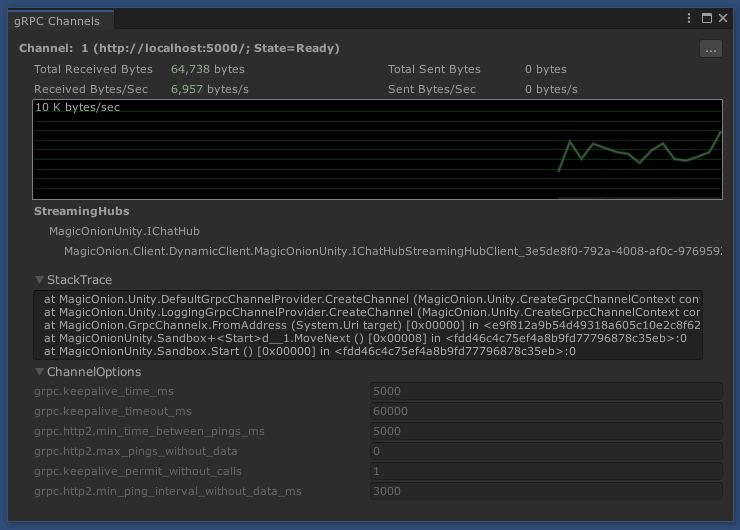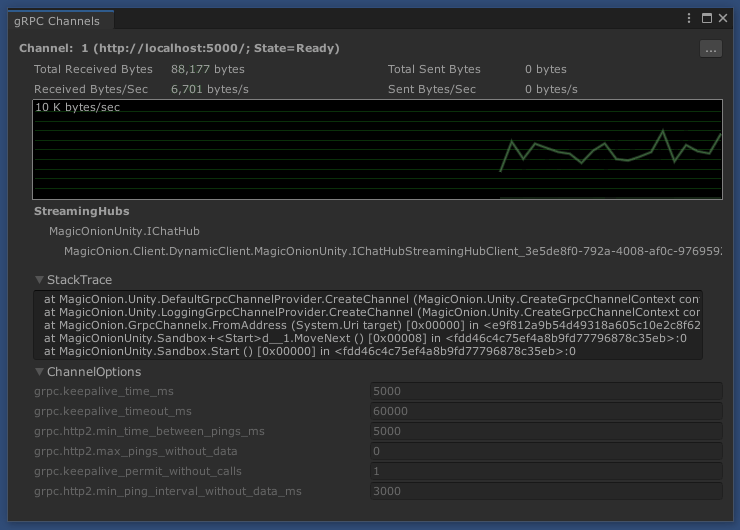
The editor extension also provides the ability to display the communication status of channels.
NOTE: The data rate is calculated only for the message body of methods, and does not include Headers, Trailers, or Keep-alive pings.
MagicOnion.GrpcChannelxclassGrpcChannelx.ForTarget(GrpcChannelTarget)methodGrpcChannelx.ForAddress(Uri)methodGrpcChannelx.ForAddress(string)method
MagicOnion.Unity.GrpcChannelProviderHostclassGrpcChannelProviderHost.Initialize(IGrpcChannelProvider)method
MagicOnion.Unity.IGrpcChannelProviderinterfaceDefaultGrpcChannelProviderclassLoggingGrpcChannelProviderclass
Before creating a channel in your application, you need to initialize the provider host to be managed.
[RuntimeInitializeOnLoadMethod(RuntimeInitializeLoadType.BeforeSceneLoad)]
public static void OnRuntimeInitialize()
{
// Initialize gRPC channel provider when the application is loaded.
GrpcChannelProviderHost.Initialize(new DefaultGrpcChannelProvider(() => new GrpcChannelOptions()
{
HttpHandler = new YetAnotherHttpHandler()
{
Http2Only = true,
},
DisposeHttpClient = true,
}));
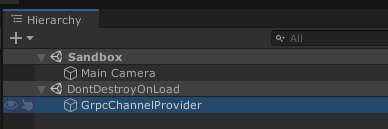
}GrpcChannelProviderHost will be created as DontDestroyOnLoad and keeps existing while the application is running. DO NOT destory it.
Use GrpcChannelx.ForTarget or GrpcChannelx.ForAddress to create a channel instead of new Channel(...).
var channel = GrpcChannelx.ForTarget(new GrpcChannelTarget("localhost", 12345, ChannelCredentials.Insecure));
// or
var channel = GrpcChannelx.ForAddress("http://localhost:12345");var channel = GrpcChannelx.ForAddress("http://localhost:12345");
var serviceClient = MagicOnionClient.Create<IGreeterService>(channel);
var hubClient = StreamingHubClient.ConnectAsync<IGreeterHub, IGreeterHubReceiver>(channel, this);When you want detect network termination on Client or vice-versa, you can configure gRPC Keepalive.
See keep alive pings | Performance best practices with gRPC | Microsoft Docs for information on setting up keepalive for Grpc.Net.Client.
MagicOnion supports TLS encrypted connection.
In general, HTTPS encryption settings on the server follow ASP.NET Core. For more information, see Enforce HTTPS in ASP.NET Core | Microsoft Docs.
NOTE: The limitations on macOS environment and when running on Docker are also described in ASP.NET Core documentation.
Depending on whether the client supports .NET Standard 2.1 or .NET Standard 2.1 (including Unity), the configuration is different.
If the client supports .NET Standard 2.1 or newer, MagicOnion uses Grpc.Net.Client (a pure C# implementation) for gRPC connection.
Grpc.Net.Client uses HttpClient internally, so it handles certificates the same way as HttpClient. For example, on Windows, it uses Windows's certificate store to validate certificates.
If the client supports .NET Standard 2.0, MagicOnion uses Grpc.Core (C-library binding) for gRPC connection.
Grpc.Core has its own certificate store built into the library and uses it unless you specify a certificate. This certificate store contains common CAs and is rarely a problem in production environment.
However, there is a problem when connecting with a server using ASP.NET Core development certificate. For example, if you see the following exceptions when you try to connect, the server certificate validation may have failed.
Grpc.Core.RpcException: 'Status(StatusCode="Unavailable", Detail="failed to connect to all addresses", ...')
The following workarounds are suggested for such cases:
- Issue and configure a trusted certificate to the server
- Use OpenSSL commands to issue and configure self-signed certificates to servers and clients
- Unencrypted connection without TLS
It is recommended to use HTTPS for server-client connection, but in some cases during development you may want to configure unencrypted connection. Also, you need to configure unencrypted connection in macOS because ALPN over TLS is not supported.
To allow your server to accept unencrypted HTTP/2, you must configure an endpoint to listen to Kestrel. Endpoints can be configured either by using appsettings.json or directly in the source code.
See also Unable to start ASP.NET Core gRPC app on macOS | Troubleshoot gRPC on .NET Core for details.
{
...
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"Grpc": {
"Url": "http://localhost:5000",
"Protocols": "Http2"
},
"Https": {
"Url": "https://localhost:5001",
"Protocols": "Http1AndHttp2"
},
"Http": {
"Url": "http://localhost:5002",
"Protocols": "Http1"
}
}
},
...
}webBuilder
.UseKestrel(options =>
{
// WORKAROUND: Accept HTTP/2 only to allow insecure HTTP/2 connections during development.
options.ConfigureEndpointDefaults(endpointOptions =>
{
endpointOptions.Protocols = HttpProtocols.Http2;
});
})
.UseStartup<Startup>();When calling GrpcChannel.ForAddress, change the URL scheme to HTTP and the port to an unencrypted port.
var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("http://localhost:5000");See also Call insecure gRPC services with .NET Core client | Troubleshoot gRPC on .NET Core | Microsoft Docs for details.
If unencrypted HTTP/2 connection is accepted, HTTP/1 and HTTP/2 cannot be served on the same port. When TLS is enabled, ALPN is used for HTTP/2 negotiation, but with non-TLS, this is not possible.
If you want HTTP/1 and HTTP/2 to work together for the convenience of hosting a web site or API, you can listen on multiple ports by configuring Kestrel.
MagicOnion is also supported in Docker containers and running on Kubernetes.
See docs/articles/deployment/ for information on deploying to Amazon Web Service and other cloud services.
MagicOnion server supports metrics related to StreamingHub using System.Diagnostics.Metrics.
| Metric | Unit | Tags |
|---|---|---|
| magiconion.server.streaminghub.connections | {connection} |
rpc.system, rpc.service |
| magiconion.server.streaminghub.method_duration | ms |
rpc.system, rpc.service, rpc.method |
| magiconion.server.streaminghub.method_completed | {request} |
rpc.system, rpc.service, rpc.method, magiconion.streaminghub.is_error |
| magiconion.server.streaminghub.exceptions | {exception} |
rpc.system, rpc.service, rpc.method, error.type |
| Tag name | Value |
|---|---|
| rpc.system | magiconion |
| rpc.service | StreamingHub interface name (e.g. IGreeterService) |
| rpc.method | StreamingHub method name (e.g. HelloAsync) |
| magiconion.streaminghub.is_error | Whether a StreamingHub method call succeeded or failed. (e.g. true or false) |
| error.type | Thrown exception type (e.g. System.InvalidOperationException) |
MagicOnion has built-in HTTP/1.1 JSON Gateway and Swagger integration for Unary operation. It can execute and debug RPC-API easily.
dotnet add package MagicOnion.Server.HttpGatewaypublic class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
services.AddGrpc(); // MagicOnion depends on ASP.NET Core gRPC service.
services.AddMagicOnion();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapMagicOnionHttpGateway("_", app.ApplicationServices.GetService<MagicOnion.Server.MagicOnionServiceDefinition>().MethodHandlers, GrpcChannel.ForAddress("https://localhost:5001"));
endpoints.MapMagicOnionSwagger("swagger", app.ApplicationServices.GetService<MagicOnion.Server.MagicOnionServiceDefinition>().MethodHandlers, "/_/");
endpoints.MapMagicOnionService();
});
}
}Open http://localhost:5000, you can see swagger view.
MagicOnionOption can pass to MagicOnionEngine.BuildServerServiceDefinition(MagicOnionOptions option).
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
IList<MagicOnionFilterDescriptor> GlobalFilters |
Global MagicOnion filters. |
bool EnableCurrentContext |
Enable ServiceContext.Current option by AsyncLocal, default is false. |
IList<StreamingHubFilterDescriptor> Global StreamingHub filters. |
GlobalStreamingHubFilters |
IGroupRepositoryFactory DefaultGroupRepositoryFactory |
Default GroupRepository factory for StreamingHub, default is ``. |
bool IsReturnExceptionStackTraceInErrorDetail |
If true, MagicOnion handles exception ownself and send to message. If false, propagate to gRPC engine. Default is false. |
MessagePackSerializerOptions SerializerOptions |
MessagePack serialization resolver. Default is used ambient default(MessagePackSerializer.DefaultOptions). |
MagicOnion can define and use primitive gRPC APIs(ClientStreaming, ServerStreaming, DuplexStreaming). Especially DuplexStreaming is used underlying StreamingHub. If there is no reason, we recommend using StreamingHub.
// Definitions
public interface IMyFirstService : IService<IMyFirstService>
{
UnaryResult<string> SumAsync(int x, int y);
Task<UnaryResult<string>> SumLegacyTaskAsync(int x, int y);
Task<ClientStreamingResult<int, string>> ClientStreamingSampleAsync();
Task<ServerStreamingResult<string>> ServerStreamingSampleAsync(int x, int y, int z);
Task<DuplexStreamingResult<int, string>> DuplexStreamingSampleAsync();
}
// Server
public class MyFirstService : ServiceBase<IMyFirstService>, IMyFirstService
{
public async UnaryResult<string> SumAsync(int x, int y)
{
Logger.Debug($"Called SumAsync - x:{x} y:{y}");
return (x + y).ToString();
}
public async Task<ClientStreamingResult<int, string>> ClientStreamingSampleAsync()
{
Logger.Debug($"Called ClientStreamingSampleAsync");
// If ClientStreaming, use GetClientStreamingContext.
var stream = GetClientStreamingContext<int, string>();
// receive from client asynchronously
await foreach (var x in stream.ReadAllAsync())
{
Logger.Debug("Client Stream Received:" + x);
}
// StreamingContext.Result() for result value.
return stream.Result("finished");
}
public async Task<ServerStreamingResult<string>> ServerStreamingSampleAsync(int x, int y, int z)
{
Logger.Debug($"Called ServerStreamingSampleAsync - x:{x} y:{y} z:{z}");
var stream = GetServerStreamingContext<string>();
var acc = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < z; i++)
{
acc = acc + x + y;
await stream.WriteAsync(acc.ToString());
}
return stream.Result();
}
public async Task<DuplexStreamingResult<int, string>> DuplexStreamingSampleAsync()
{
Logger.Debug($"Called DuplexStreamingSampleAsync");
// DuplexStreamingContext represents both server and client streaming.
var stream = GetDuplexStreamingContext<int, string>();
var waitTask = Task.Run(async () =>
{
// ForEachAsync(MoveNext, Current) can receive client streaming.
await foreach (var x in stream.ReadAllAsync())
{
Logger.Debug($"Duplex Streaming Received:" + x);
}
});
// WriteAsync is ServerStreaming.
await stream.WriteAsync("test1");
await stream.WriteAsync("test2");
await stream.WriteAsync("finish");
await waitTask;
return stream.Result();
}
}Client sample.
static async Task ClientStreamRun(IMyFirstService client)
{
var stream = await client.ClientStreamingSampleAsync();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
await stream.RequestStream.WriteAsync(i);
}
await stream.RequestStream.CompleteAsync();
var response = await stream.ResponseAsync;
Console.WriteLine("Response:" + response);
}
static async Task ServerStreamRun(IMyFirstService client)
{
var stream = await client.ServerStreamingSampleAsync(10, 20, 3);
await foreach (var x in stream.ResponseStream.ReadAllAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine("ServerStream Response:" + x);
}
}
static async Task DuplexStreamRun(IMyFirstService client)
{
var stream = await client.DuplexStreamingSampleAsync();
var count = 0;
await foreach (var x in stream.ResponseStream.ReadAllAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine("DuplexStream Response:" + x);
await stream.RequestStream.WriteAsync(count++);
if (x == "finish")
{
await stream.RequestStream.CompleteAsync();
}
}
}In RPC, especially in real-time communication involving frequent transmission of data, it is often the serialization process where data is converted before being sent that limits the performance. In MagicOnion, serialization is done by my MessagePack for C#, which is the fastest binary serializer for C#, so it cannot be a limiting factor. Also, in addition to performance, it also provides flexibility regarding data in that variables of any type can be sent as long as they can be serialized by MessagePack for C#.
Also, taking advantage of the fact that both the client and the server run on C# and data stored on internal memory are expected to share the same layout, I added an option to do mapping through memory copy without serialization/deserialization in case of a value-type variable.
Especially in Unity, this is can combinate with MessagePack.UnityShims package of NuGet.
// It supports standard struct-type variables that are provided by Unity, such as Vector3, and arrays containing them, as well as custom struct-type variables and their arrays.
// I recommend doing this explicitly using [StructLayout(LayoutKind.Explicit)] to accurately match the size.
public struct CustomStruct
{
public long Id;
public int Hp;
public int Mp;
public byte Status;
}
// ---- Register the following code when initializing.
// By registering it, T and T[] can be handled using zero deserialization mapping.
UnsafeDirectBlitResolver.Register<CustomStruct>();
// The struct-type above as well as Unity-provided struct-types (Vector2, Rect, etc.), and their arrays are registered as standards.
CompositeResolver.RegisterAndSetAsDefault(
UnsafeDirectBlitResolver.Instance,
MessagePack.Unity.Extension.UnityBlitResolver.Instance
);
// --- Now the communication will be in the format above when they are used for transmission.
await client.SendAsync(new CustomStruct { Hp = 99 });Nothing needs to be processed here, so it promises the best performance theoretically possible in terms of transmission speed. However, since these struct-type variables need to be copied, I recommend handling everything as ref as a rule when you need to define a large struct-type, or it might slow down the process.
I believe that this can be easily and effectively applied to sending a large number of Transforms, such as an array of Vector3 variables.
MagicOnion uses MessagePack for serialization by default, but it also provides extension points to customize serialization.
It allows for customization, such as encryption and the using of serializers other than MessagePack.
/// <summary>
/// Provides a serializer for request/response of MagicOnion services and hub methods.
/// </summary>
public interface IMagicOnionSerializerProvider
{
IMagicOnionSerializer Create(MethodType methodType, MethodInfo? methodInfo);
}
/// <summary>
/// Provides a processing for message serialization.
/// </summary>
public interface IMagicOnionSerializer
{
void Serialize<T>(IBufferWriter<byte> writer, in T? value);
T? Deserialize<T>(in ReadOnlySequence<byte> bytes);
}
public static class MagicOnionSerializerProvider
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the <see cref="IMagicOnionSerializerProvider"/> to be used by default.
/// </summary>
public static IMagicOnionSerializerProvider Default { get; set; } = MessagePackMagicOnionSerializerProvider.Default;
}The following code is a simple example of performing XOR encryption:
public class XorMessagePackMagicOnionSerializerProvider : IMagicOnionSerializerProvider
{
const int MagicNumber = 0x11;
readonly MessagePackSerializerOptions serializerOptions;
public static IMagicOnionSerializerProvider Instance { get; } = new XorMessagePackMagicOnionSerializerProvider(MessagePackSerializer.DefaultOptions);
XorMessagePackMagicOnionSerializerProvider(MessagePackSerializerOptions serializerOptions)
=> this.serializerOptions = serializerOptions;
class XorMessagePackMagicOnionSerializer : IMagicOnionSerializer
{
readonly MessagePackSerializerOptions serializerOptions;
public XorMessagePackMagicOnionSerializer(MessagePackSerializerOptions serializerOptions)
{
this.serializerOptions = serializerOptions;
}
public T Deserialize<T>(in ReadOnlySequence<byte> bytes)
{
var array = ArrayPool<byte>.Shared.Rent((int)bytes.Length);
try
{
bytes.CopyTo(array);
for (var i = 0; i < bytes.Length; i++)
{
array[i] ^= MagicNumber;
}
return MessagePackSerializer.Deserialize<T>(array.AsMemory(0, (int)bytes.Length), serializerOptions);
}
finally
{
ArrayPool<byte>.Shared.Return(array);
}
}
public void Serialize<T>(IBufferWriter<byte> writer, in T value)
{
var serialized = MessagePackSerializer.Serialize(value, serializerOptions);
for (var i = 0; i < serialized.Length; i++)
{
serialized[i] ^= MagicNumber;
}
writer.Write(serialized);
}
}
public IMagicOnionSerializer Create(MethodType methodType, MethodInfo? methodInfo)
=> new XorMessagePackMagicOnionSerializer(serializerOptions);
}MagicOnion also supports MemoryPack as a message serializer. (preview)
dotnet add package MagicOnion.Serialization.MemoryPack
Set MemoryPackMagicOnionSerializerProvider to MagicOnionSerializerProvider on the client and server to serialize using MemoryPack.
MagicOnionSerializerProvider.Default = MemoryPackMagicOnionSerializerProvider.Instance;
// or
await StreamingHubClient.ConnectAsync<IMyHub, IMyHubReceiver>(channel, receiver, serializerProvider: MemoryPackMagicOnionSerializerProvider.Instance);
MagicOnionClient.Create<IMyService>(channel, MemoryPackMagicOnionSerializerProvider.Instance);If you want to use MagicOnion.Client.SourceGenerator, you need to specify Serializer = GenerateSerializerType.MemoryPack to the attribute. The generated code will use MemoryPack instead of MessagePack.
The application must also call MagicOnionMemoryPackFormatterProvider.RegisterFormatters() on startup.
This library is under the MIT License.