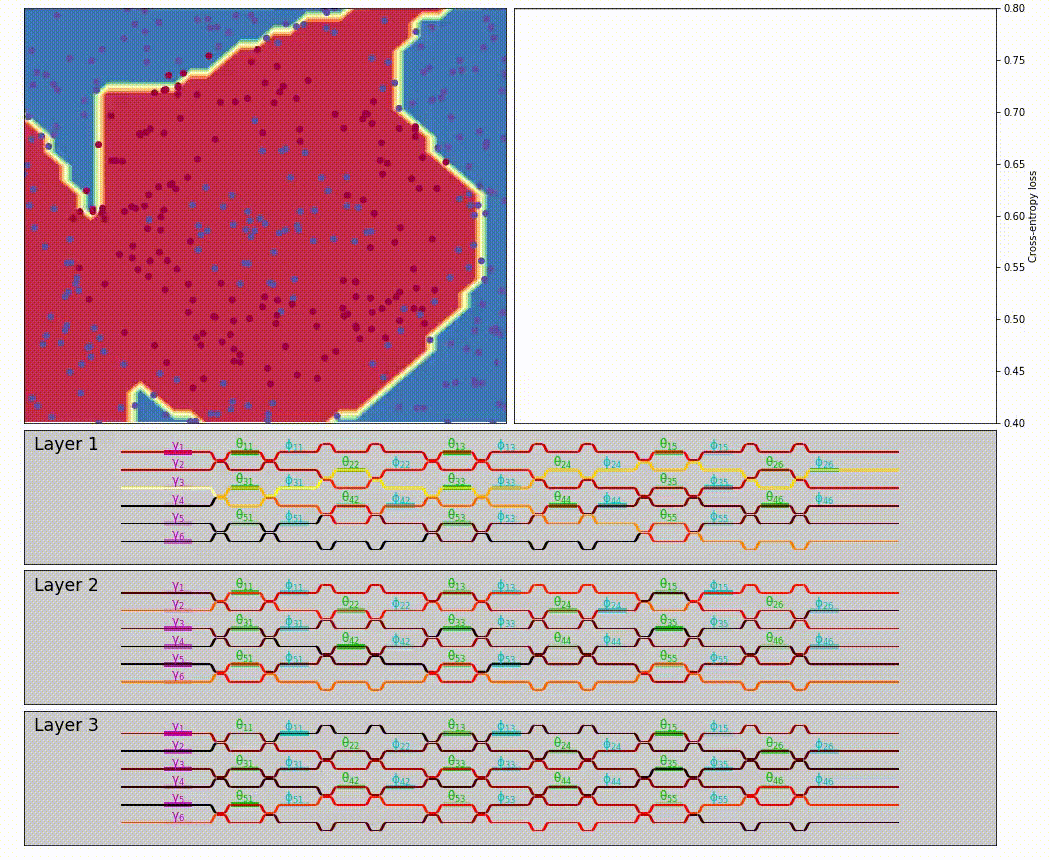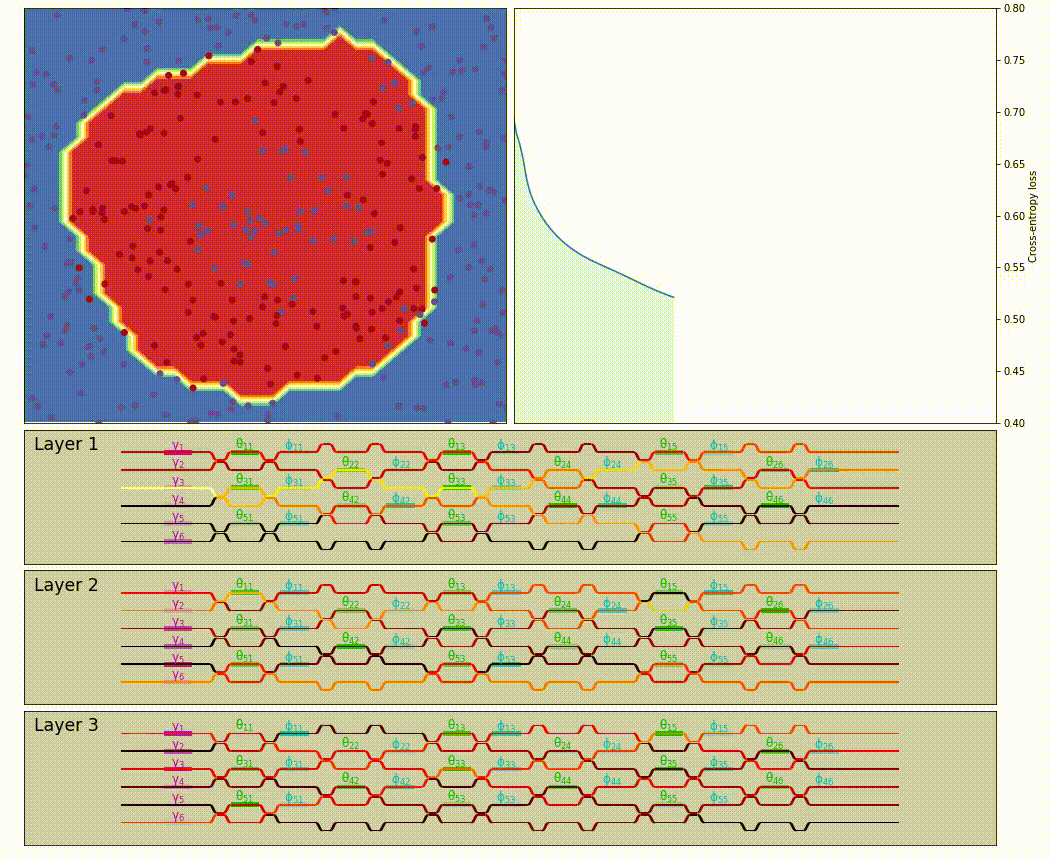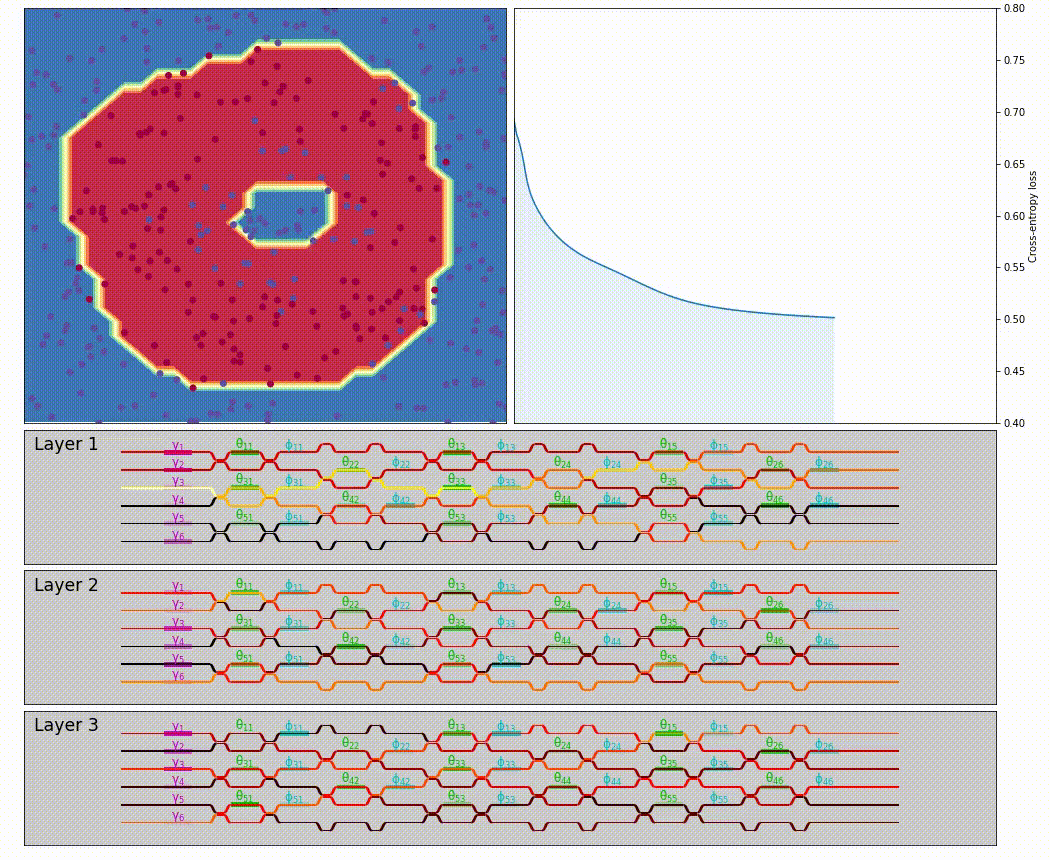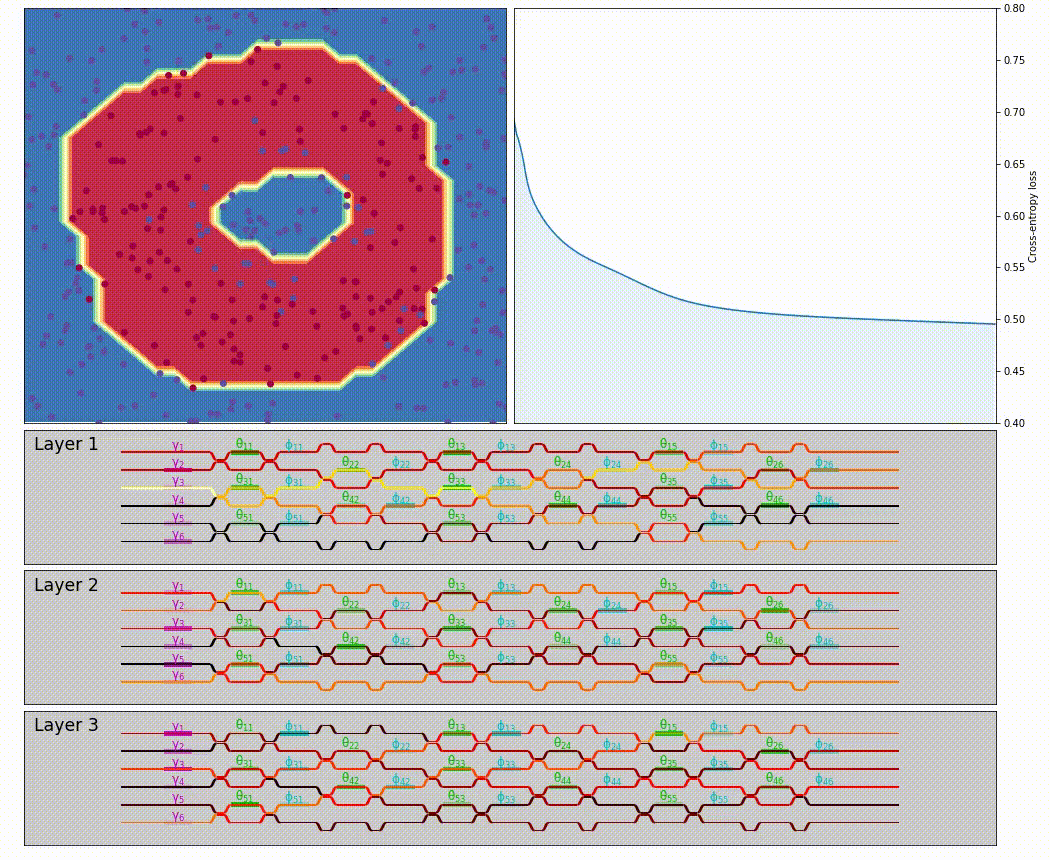
neuroptica is a flexible chip-level simulation platform for nanophotonic neural networks written in Python/NumPy. It provides a wide range of abstracton levels for simulating optical NN's: the lowest-level functionality allows you to manipulate the arrangement and properties of individual phase shifters on a simulated chip, and the highest-level features provide a Keras-like API for designing optical NN by stacking network layers.
The easiest way to get started with neuroptica is to install directly from the Python package manager:
pip install neuroptica
Alternately, you can clone the repository source code and edit it as needed with:
git clone https://github.com/fancompute/neuroptica.git
pip install -e neuroptica
To run unit tests, use - python -m unittest discover -v from the root package directory.
For an overview of neuroptica, read the documentation. Example notebooks are included in the neuroptica-notebooks repository:
neuroptica was written by Ben Bartlett, Momchil Minkov, Tyler Hughes, and Ian Williamson. If you find this useful for your research, please cite the GitHub repository and/or the JSQTE paper:
@misc{Bartlett2019Neuroptica,
author = {Ben Bartlett and Momchil Minkov and Tyler Hughes and Ian A. D. Williamson},
title = {Neuroptica: Flexible simulation package for optical neural networks},
year = {2019},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/fancompute/neuroptica}},
commit = {06484f698ee038eeb128cdfbd4c59a7e96185bb4}
}
@article{Williamson2019Reprogrammable,
author={I. A. D. Williamson and T. W. Hughes and M. Minkov and B. Bartlett and S. Pai and S. Fan},
journal={IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics},
title={Reprogrammable Electro-Optic Nonlinear Activation Functions for Optical Neural Networks},
year={2020},
volume={26},
number={1},
pages={1-12}
}